Ammonium Paratungstate Used in Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Production
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 03 February 2021 19:32
Electrochemical hydrogen evolution from water splitting for hydrogen production as a sustainable and environmentally friendly strategy has drawn great attention in recent years. Currently Pt-based materials is the most efficient electrocatalysts toward hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), but the inexpensive cost has limited their widespread applications. Finding an efficient and inexpensive substitute HER catalysts is in need.
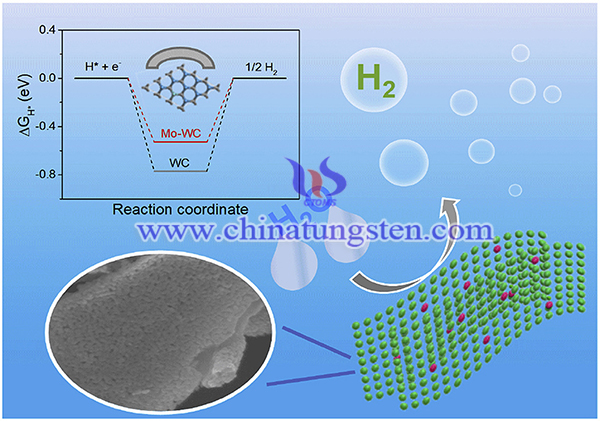
Hence, ammonium paratungstate (APT) and ammonium molybdate have been used in electrocatalyst for hydrogen production. An electrocatalyst has been created with Mo-doped WC (Mo-WC) core embedded within N-doped carbon shells (NCS). Th Mo-WC@NCS electrocatalyst showed an excellent HER activity for hydrogen production. The synthesis process and characterization of the Mo-WC@NCS electrocatalyst are as below:
Solution A was obtained by adding a certain amount of ammonium molybdate, 0.5 g of ammonium paratungstate, 1.3 g of dimethyl imidazole, and deionized water (DI) simultaneously under stirring for 4 h. Solution B was obtained by adding 0.6 g of zinc nitrate hexahydrate into 20 mL of DI water. Then, the solution B was slowly poured into the solution A with further stirring for 4 h. The obtained mixture was collected by centrifuged and washed three times with DI water. The product was further annealed in a tube furnace at 900 °C under H2 atmosphere for 1 h with the rate of 5 °C min−1. After cooling down to the room temperature, black powder was collected by centrifuged and washed with DI water.
The result product was firstly characterized with X-ray diffraction (XRD) field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) Raman spectra were obtained from LabRAM HR Evolution with a wavelength of 532 nm; Secondly, Electrocatalytic activities of as-prepared samples were assessed by a three-electrode cell, where an Ag/AgCl electrode, the sample modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE), and a graphite rod were used as reference electrode, working electrode, and counter electrode, respectively. All data are presented with iR compensation and the potentials are referenced to a reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) by adding a value of (0.197 + 0.0591 × pH) V. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) test was carried out in the frequency range of 105–0.01 Hz with an AC amplitude of 0.01 V.
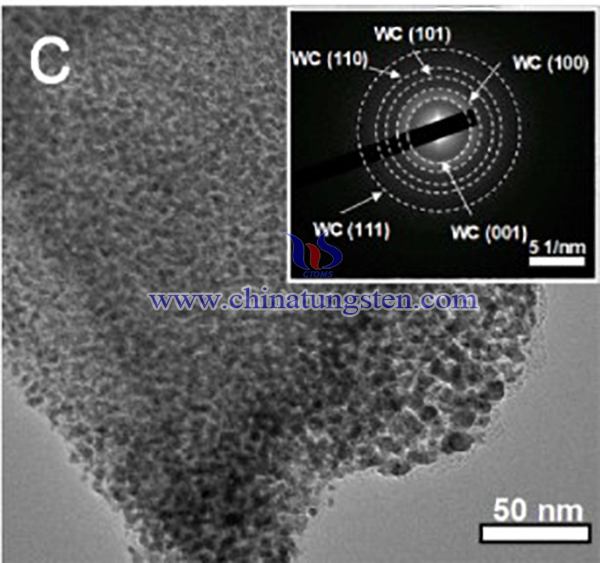
In summary, ammonium paratungstate (APT) and ammonium molybdate have been used in electrocatalyst for hydrogen production. A hybrid electrocatalyst consisting of Mo doped WC cores encapsulated into N-doped carbon shells for HER has been successfully produced. Mo-WC core with particle size of ~5 nm was encapsulated within NCS with average thickness of ~50 nm. the achieved Mo-WC@NCS hybrid displayed an excellent HER activity with a low overpotential of 179 mV at 10 mA cm−2 and a small Tafel slope of 81 mV dec−1.
- APT Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: ammonium-paratungstate.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com