Tungsten Carbide Inhibitor Composite Powder
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 07 August 2019 13:41
Ultra-fine grained tungsten carbide-based hard alloy has high strength and high hardness "double high" performance, which can be used in the production of printed circuit board micro drill bits, dot matrix printer printing needles, precision tooling, and difficult material tools.
The industry believes that when the grain size of tungsten carbide is reduced and the distribution of cobalt in the binder phase is highly uniform, the number and size of defects will be reduced or even zero, and the mechanical properties of the alloy can be much higher than that of ordinary cemented carbide. There are two key processes for the preparation of ultrafine grained WC-based cemented carbides: one is the preparation of WC or WC-Co raw material powder with fine grain and fine distribution; the other is the growth inhibition of WC grains during sintering.
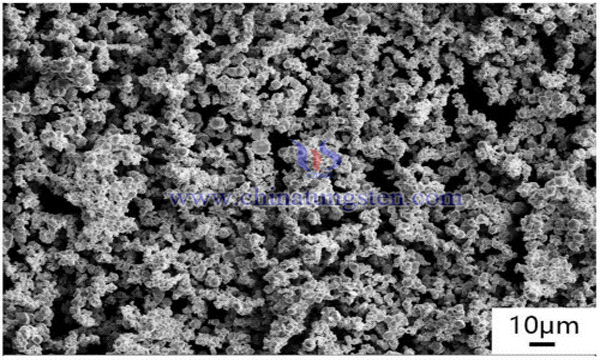
Based on the consideration of cost and process, people tend to solve the problem in the second way. At this stage, most of the growth inhibition of WC grains during sintering is mainly studied by the researchers in the synthesis of WC-based composite powder in liquid phase. Or adding a grain growth inhibitor (such as vanadium carbide (VC), chromium carbide (Cr3C2), tantalum carbide (TaC), when the WC powder is mixed with a metal powder such as cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), or iron (Fe). It is realized by niobium carbide (NbC) or the like. The disadvantage is that vanadium carbide and the like having a low carbonization temperature do not fundamentally solve the problem that it is difficult to uniformly disperse, and chromium, antimony, etc. are difficult to be completely carbonized, and a small amount of oxide or carbon-deficient phase still exists in the WC matrix, and must be used. The other way is perfect.
Some scholars have proposed a preparation method of tungsten carbide inhibitor composite powder. The method uses a tungsten oxide (or salt) and an inhibitor oxide (or salt) as a raw material to reduce and carbonize the WC inhibitor composite powder in one step, and the products are all carbides, and the process is easy to control and is not limited by the type of raw materials. The specific experimental operations include:
(1) Matching ratio:
Ammonium metatungstate AMT, ammonium metavanadate and ammonium dichromate are miscible in distilled water at a mass ratio of 100:0.66:0.74, and are spray pyrolyzed to form an oxide powder.
(2) Ball milling process
Using one or more of ethanol, acetone, and hexane as a medium for wet grinding, and dry grinding in a roller ball mill for 72 hours, the ambient atmosphere is an inert gas, or a vacuum;
(3) Sintering process
The obtained mixed powder is carbonized in a tube furnace in an argon atmosphere at 1350 ° C for 0.5 hours, and then cooled to room temperature in an argon atmosphere, and the sintering method is vacuum sintering, or hydrogen gas sintering, the gas is argon gas or nitrogen gas;
(4) Heat treatment process
The heat treatment method is hot isostatic pressing or low pressure, wherein the hot isostatic pressing atmosphere is argon or nitrogen, the temperature is 1200 to 1350 ° C, the pressure is 100 to 200 MPa; the low pressure heat treatment atmosphere is argon or nitrogen, and the temperature is 1250 ~ 1400 ° C, the pressure is 3 ~ 7MPa.
At the same time, the comparative experiment was carried out in the furnace: using WO3+C, V2O5+C, Cr2O3+C three other prepared raw materials, the results show that at the carbonization temperature of 1350 °C, the inhibitor oxide raw materials can be carbonized into the desired Inhibitor carbide; compared with the prepared WC-inhibitor composite powder and pure WC powder, the characteristic peaks of the two are exactly the same, except that the inhibitor is not detected due to the small amount.
The SEM and TEM photographs of the ultrafine WC-12Co-0.4VC-0.4Cr3C2 hard alloy prepared from the tungsten carbide inhibitor composite powder show that the grain size of the cemented carbide is uniform, no macropores, cobalt pool, In the carbon-deficient or carburized zone, most of the crystal grains have a rectangular shape with a length of 0.3 to 0.5 μm and a width of 0.1 to 0.2 μm. It can be seen from the results that the method basically solves the defects in the prior art that the inhibitor is added late or the inhibitor can only use the inhibitor with low carbonization temperature in the early stage, the process is simple and safe, the production cost is low, and the industrialization is easy.
- Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com