The Preparation process of High-efficiency Copper-VOT Photocatalysts
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 29 May 2019 01:20
With the increasing problems of energy and environment, the pollution of water resources by organic matter is particularly prominent, which not only affects human health, but also consumes a large amount of energy to eliminate such pollutants. Therefore, the development of new materials using photocatalytic technology to solve pollution has become a new research direction.
At present, methods for preparing a transition metal doped photocatalyst material mainly include a sol-gel method, a hydrothermal method, a precipitation method, a microemulsion method, a gas phase method, and the like. However, some of the above methods have a long preparation time, and some methods have problems such as particle size and distribution, uneven pore structure, and high cost of preparing catalysts. Therefore, there is a need to develop new low-cost, high-efficiency photocatalysts.
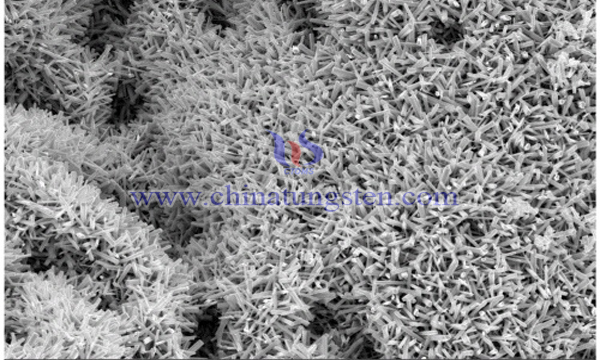
Among many catalyst materials, violet tungsten oxide (VTO) has a special surface structure, high chemical activity, large concentration of oxygen-deficient structure, and a high degree of absorption in ultraviolet light. At the same time, studies have shown that copper as a doping element can be very good. Improve the response of the catalyst in the visible range. Therefore, the choice of copper-VOT photocatalyst as a photocatalytic material has a good application prospect.
The copper-VOT photocatalyst can be carried out by the simplest hydrothermal method, and its contents include:
1. Raw materials: The raw materials used are VOT, copper, ammonium nitrate and adjuvants.
2. Solution preparation: The selected raw materials are formulated into a solution according to a certain ratio and uniformly mixed.
3. Precursor preparation: The aqueous solution obtained in step 2 is heated, and as the aqueous solution is volatilized, the solution is bubbled after concentration, a large amount of gas is released, and a vigorous redox reaction occurs in several tens of seconds to form a copper-VOT powder. The obtained powder was in the form of a nanoneedle having a diameter of 50 to 150 nm and a length of 1 to 3 μm. The catalyst with a concentration of 1 g/L was applied to the degradation of methylene blue, an organic pollutant of 20 ppm, and the degradation rate was 92% at around 35 minutes.
Using tungstate (ammonium metatungstate) and copper nitrate as raw materials, copper-doped purple tungsten powder is directly synthesized by hydrothermal method, which is applied to photocatalysis, has low cost and high efficiency, and is suitable for large-scale production.
- AMT Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: ammonium-metatungstate.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com