Process of Liquid Phase Sintering
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 02 March 2018 21:37
Tungsten carbide has many important applications in industry, of which the sintering has also undergone many technological innovations. Sintering of the tungsten carbide belongs to multicomponent liquid phase sintering. During the sintering process, the bonded metal melted and formed a low melting eutectic, which is different from the solid-state sintering system. The process of liquid phase sintering will undergo a period of three distinct boundaries.
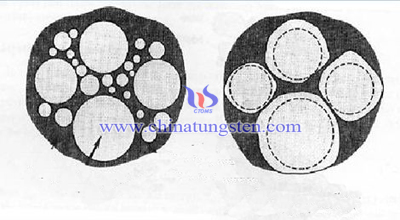
1, Stage of Liquid Phase Flow and Particle Rearrangement
When the temperature is higher than the melting point or eutectic point of the liquid component, the liquid phase is formed. Then the liquid phase flows and fills the pores under the action of the capillary force. Relative movement of particles will not occur during solid phase sintering.
Particles are approximately suspended in the liquid phase with the existence of liquid phase. It is moved by the surface tension of the liquid phase. Therefore, the wetting of liquid to solid particles and the existence of sufficient liquid phase are important preconditions for the movement of particles.
The capillary force formed by the liquid phase in the intergranular pore and the viscous flow of the liquid itself, so as to adjust the position and redistribution of the particles to achieve the closest arrangement. At this stage, the density of the sintered body increases rapidly.
2, Stage of Solid Dissolution and Reprecipitation
Atoms on the surface of a solid particle gradually dissolve in the liquid phase, of which the solubility changes with the change of temperature and the shape and particles size. The liquid has a larger saturated solubility relative to the small particles. Due to the large surface area of the small particles, the surface energy is higher and easier to dissolve first. Meanwhile, the edges and corners of the particles and the convex parts (larger curvature) are also preferentially dissolved.
Therefore, the small particles tend to decrease, and the surface of the particles tend to be smooth and smooth. On the contrary, the saturated solubility of large particles is lower, so that a part of the supersaturated atom in the liquid phase is precipitated on the surface of the large particles, making the large particles grow up. This is the solution and re precipitation of the solid phase, that is, the process of material migration through the liquid phase, and the velocity of densification slows down compared with the first stage.
3, Stage of Solid State Sintering
After two stages of particle rearrangement and dissolution, the particles close together. While the particles contact surface, solid phase sintering is formed, making the particles glued to each other. After the growth of the sintered neck and the spheroidization and reduction of closed pores, the solid skeleton is formed. At this time, the remaining liquid phase is filled with the gap of the skeleton. And the densification has slowed down significantly.
- Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com