Tungsten Oxide Non-Stoichiometric Structure Principle
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 06 February 2018 12:33
Tungsten oxide, as an intermediate oxide of tungsten, is different from a compound having a classical stoichiometric structure and has a composition deviating from the integrality and point defects.
It is very important in modern materials science and solid chemistry Status, rather than stoichiometric compounds (chemical composition of the chemical composition of the crystal structure with different atoms occupy the ratio does not match) is another example of tungsten oxide solid chemical core, directly determines the tungsten oxide Light, electricity, heat, sound and magnetic properties. Therefore, the principle of exploring the formation of non-stoichiometric tungsten oxide structure is very necessary.
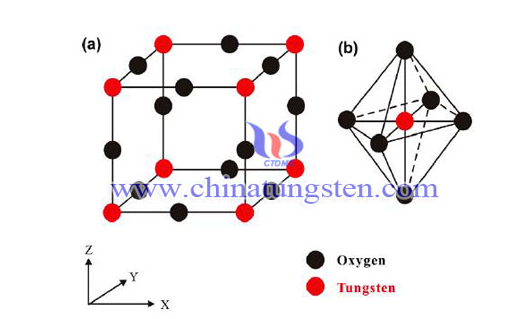
Point defects (a defect that deviates from the normal arrangement of crystal structures in or near the microscopic area) are important causes for the formation of non-stoichiometric tungsten oxide structures and have three major drawbacks in the classification of point defects: The first one is the ion or atom defect, which is the excess (deficiency) of a component ion or atom in the formation of tungsten oxide, resulting in the excess ions or atoms occupying the normal position of the tungsten oxide crystal lattice (or causing vacancy formation defects) .
The second is the partial replacement of impurity ions defects, that is, when there is tungsten oxide composition similar to the ionic structure, the smaller the radius and the electronegativity of similar substances, the substitution effect occurs between the two; the third is interstitial Defects, that is, tungsten oxide crystals interstitial randomly filled with smaller atoms or ions, making the material itself a certain change in the structure. These three kinds of point defects do not exist in isolation but blend with each other and infiltrate each other.
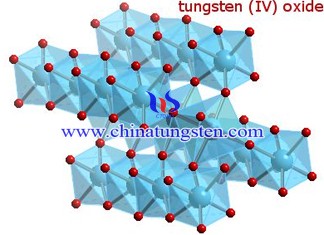
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com