Effects of Pre-Sintering Temperature on Tungsten Carbide Density
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 13 November 2017 14:03
The pre-sintering temperature of tungsten carbide has a direct effect on the density. With the pre-sintering temperature increasing, the overall density of the green is increasing. But the change trend is different in different temperature range. When the temperature is low, the change depends on the density of volatile forming agent. At high temperatures, it depends mainly on the diffusion of atoms.
Tendency of Pre-Sintering Density Change
Effects of pre-sintering temperature on the sintering density as shown below. A curve shows the density after sintering at different temperatures, while B curve shows initial compaction density of green sample. It can be seen from the figure, with the increase of sintering temperature, density of pre-sintered green increases.
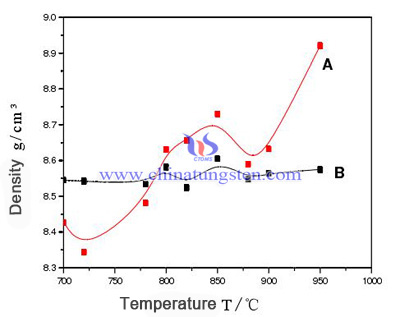
Mechanism of Pre-Sintering
According to the sintering mechanism of cemented carbide, sintering at low temperature range of 700 ~ 950℃ is low temperature solid state sintering. The density of pre sintered billets decreases at first and then increases at 700 ~ 820℃, which may be due to the volatilization of the molding agent resulting in a decrease in density at low temperatures.
Because the forming agent volatilization between powder particles and particles contact stress gradually eliminated, bond began to produce metal powder recovery and recrystallization, and produced the original hole forming agent volatilization is not eliminated, the compact expansion, compact expansion also led to decline in density. When the temperature reaches 720℃, forming agent is decomposed completely, so the density is reduced to the minimum value of 8.34g/cm³.
The diffusion of surface atoms has begun to occur in 400℃, but the rate of atomic diffusion is very low, so the change in the low temperature sintering compacts density depends on the volatilization of forming agent. When the temperature is higher than 720℃, the diffusion of surface atoms begins to increase, and the density of the compacts begins to rise. When the temperature is 790℃, the density of pre-sintered compacts is equal to the initial density.
As the temperature continues to rise, the "welding" phenomenon occurs between the cobalt powder particles and the particles, and the compacts begin to produce certain shrinkage. Sintering shrinkage resulting in high density, therefore the pre sintering temperature at 720 to 850℃, pre sintered compact density has been rising. The density of pre-sintered billets once again decreases first and then increases, which may be related to the original compacts, on the other hand, to the expansion of pre-sintered compacts.
Due to the increase of temperature, the counterdiffusion between atoms intensifies, and the diffusion of cobalt atoms to WC particles. There were some micropores in the area where the cobalt powder existed, so the pre-sintered billet appeared expansion.
When the temperature increases further, some of the cobalt particles begin to melt and fill these micropores, and the sintered compacts begin to contract. When the temperature is higher than 900℃, the density increases rapidly, indicating that the diffusion is further intensified, and the density and strength of the pre sintered compacts are significantly improved.
- Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com