Thermal Stability of Tungsten Disulfide in Gaseous Mediums
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 24 September 2019 19:11
- Written by Yanqiu
- Hits: 1347

Thermal stability of tungsten disulfide varies in different gaseous mediums or gas states. Tungsten disulfide can be heated and react not only in air but also in vacuum. Usually, hydrogen, argon and nitrogen are needed in the preparation of tungsten disulfide.
.jpg)
Thermal stability, also known as heat resistance, refers to the deformation capacity of substance under the influence of temperature. The smaller the deformation, the higher the thermal stability. Generally, we can judge the thermal stability of a substance by observing the phenomena during the heating.
Thermal stability of tungsten disulfide is as follows:
1. In air (O2)
When heated in air, tungsten disulfide reacts with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide and tungsten trioxide with low friction coefficient. The higher temperature and the smaller tungsten disulfide particles lead to the more active reaction.
2. In vacuum
When heated in vacuum, tungsten disulfide can release a small amount of gas. It can slowly decompose into sulfur and tungsten when heated to above 1100°C. And when heated to 1250°C, it is decomposed completely.
.jpg)
3. Hydrogen (H2)
Tungsten disulfide produces tungsten and hydrogen sulfide when heated to about 80°C in hydrogen. The chemical reaction is as follows:
1/2 WS2 (solid) +H2 (gas) ←→H2S (gas) +1/2 W (solid)
The relationship of the equilibrium constant K and reaction temperature T at low temperature is different from that at high temperature, which is caused by different crystalline states of tungsten disulfide.
4. Nitrogen (N2)
Tungsten disulfide is stable in nitrogen.
5. Argon (Ar)
Tungsten disulfide loses a small amount of sulfur when heated to more than 1000°C in argon.
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com
Batch Synthesis of Tungsten Trioxide Nanosheets
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 23 September 2019 22:48
- Written by meiwei
- Hits: 1314
Nanomaterials have become one of the hotspots of current research due to their unique physical and chemical properties, such as high specific surface area, quantum size effect, small size effect and macroscopic quantum tunneling effect. In recent years, many Nano-Research centers have been established in China, and some remarkable achievements have been made in catalysis, gas sensing and other fields.
One-step Hydrothermal Method of Tungsten Oxide Quantum Dots and Tungsten Oxide Nanowires
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 23 September 2019 22:20
- Written by meiwei
- Hits: 1431
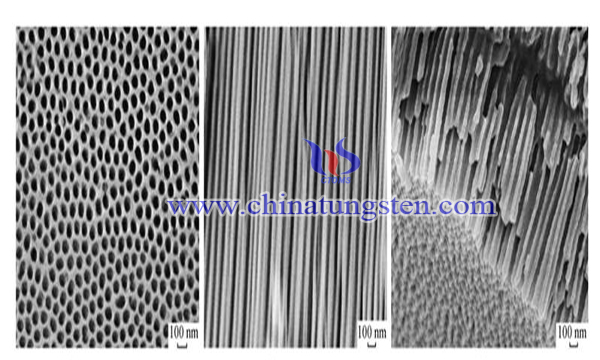
Tungsten oxide is a kind of tungstic anhydride and a kind of tungstate product. Tungsten oxide includes trioxide and tungsten dioxide. Tungsten oxide is partly used in the production of chemical products, such as paints and coatings, petroleum industrial catalysts, etc. But tungsten oxide is more an intermediate product and is widely used in the preparation of tungsten metal powder and tungsten carbide powder. It is used in the production of tungsten metal products and a large number of tungsten alloy products.
Read more: One-step Hydrothermal Method of Tungsten Oxide Quantum Dots and Tungsten Oxide Nanowires
Copper-supported Tungsten Oxide Nanotubes
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 23 September 2019 22:33
- Written by meiwei
- Hits: 1354

In the field of semiconductor photocatalysis, titanium dioxide has been widely studied, but its bandgap is wide (3.2ev). Only ultraviolet light can excite it to produce photogenerated carriers. In sunlight, the proportion of ultraviolet light is very small, so the utilization of sunlight in pure titanium dioxide photocatalysis process is very low.
Tungsten Oxide Photocatalyst Loaded with Platinum Particles on the Surface
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 23 September 2019 22:05
- Written by meiwei
- Hits: 1329

When a semiconductor irradiates light with energy above bandgap, the electrons of valence band excite in the conduction band, generate holes in the valence band, and generate electrons in the conduction band. They have strong oxidation and reduction abilities respectively, and have redox effects on molecular species in contact with semiconductors. Such an action is called photocatalysis, and such semiconductors are called photocatalysts.
Read more: Tungsten Oxide Photocatalyst Loaded with Platinum Particles on the Surface





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com