Classification of Tungsten Alloy Shielding Components
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 12 August 2025 15:29
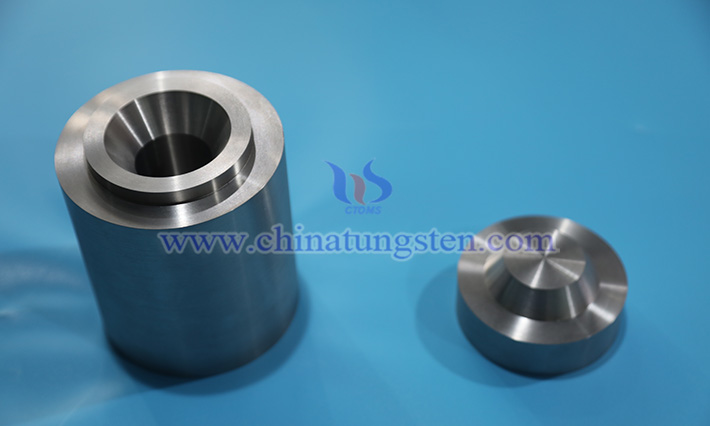
As a representative of high-density materials, tungsten alloy shielding components, with their high density, excellent radiation attenuation effect, heat resistance, strong mechanical strength, and environmental friendliness, are widely used in radiation protection applications in medical, industrial, nuclear engineering, and scientific research fields. Depending on their design shapes, tungsten alloy shielding components can be classified into plate-like shielding components, tubular shielding components, container-like shielding components, and complex geometric shielding components.
What Is Tungsten Alloy Shielding Plate?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 12 August 2025 15:24
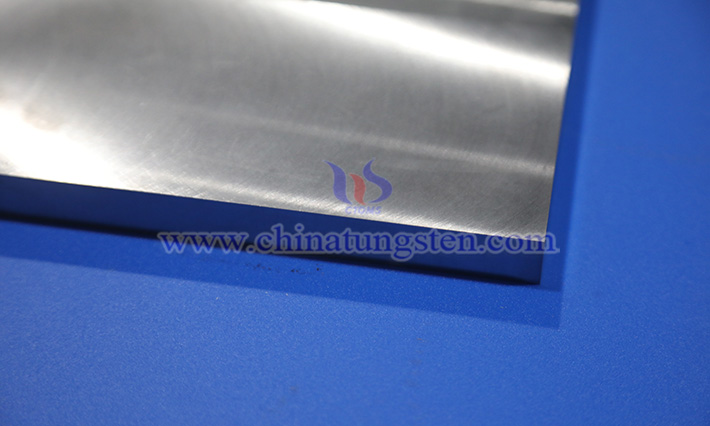
Tungsten alloy shielding plate is a plate-like structural component primarily composed of tungsten (typically containing 85% to 99% tungsten, with additional elements such as nickel, iron, or copper), used for radiation protection and shielding ionizing radiation (such as gamma rays, X-rays, or neutron radiation). Thanks to its high specific gravity, excellent radiation attenuation performance, heat resistance, mechanical strength, and environmental friendliness, the tungsten alloy shielding plate has become an ideal alternative to traditional lead materials in medical, industrial, nuclear engineering, and scientific fields. Compared to lead, it achieves equivalent shielding effects at a thinner thickness, reducing material usage and equipment weight, while being non-toxic, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for long-term use.
Applications of Tungsten Alloy Collimators in the Medical Field
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 12 August 2025 15:18
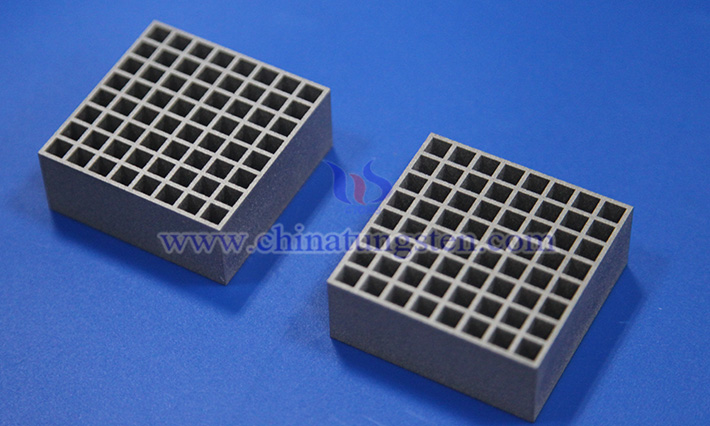

The application of tungsten alloy collimators in the medical field primarily focuses on diagnostic imaging and radiotherapy, owing to their high density, excellent radiation attenuation performance, heat resistance, and mechanical strength, making them essential components in medical equipment. Compared to traditional lead materials, tungsten alloy is more environmentally friendly, offers higher shielding efficiency, and enables thinner, lighter designs, making it ideal for space-constrained devices.
Applications of Tungsten Alloy Collimator
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 12 August 2025 15:14
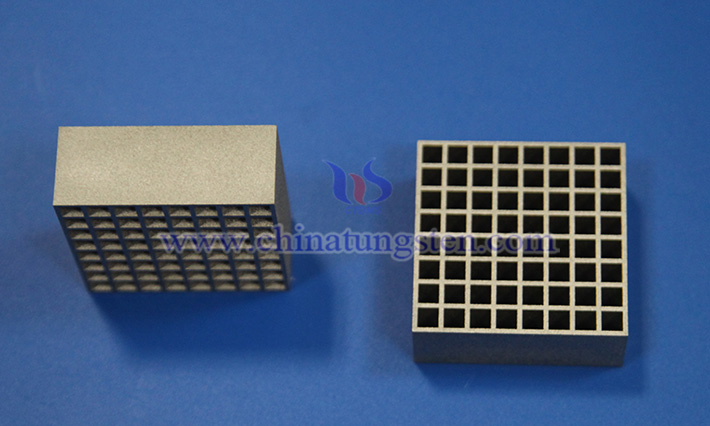
Tungsten alloy collimator is an optical or radiation control device made from tungsten alloy material, primarily used to guide and limit the direction and range of particle beams, wave beams, or radiation beams. Renowned for its high density, excellent radiation attenuation performance, heat resistance, and mechanical strength, it outperforms lead materials in efficiency and environmental friendliness, with applications spanning medical, industrial, and scientific fields.
Tungsten Wire for Composite Material Stiffeners
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 11 August 2025 19:22
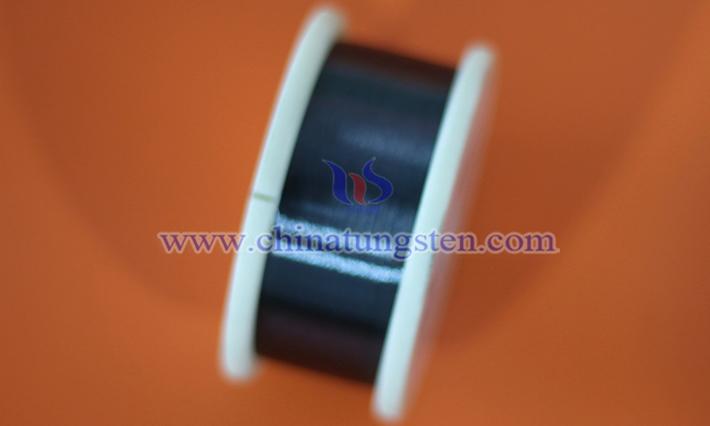

The use of tungsten wire as a reinforcing element in composite material stiffeners represents a high-performance material solution that combines the characteristics of tungsten wire—high strength, high modulus, and high-temperature resistance—with the advantages of composite materials, such as lightweight and strong design flexibility. Below is a detailed analysis of the application of tungsten wire in composite material stiffeners:
Applications of Tungsten Wire as Reinforcement in Composite Materials
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 11 August 2025 19:17
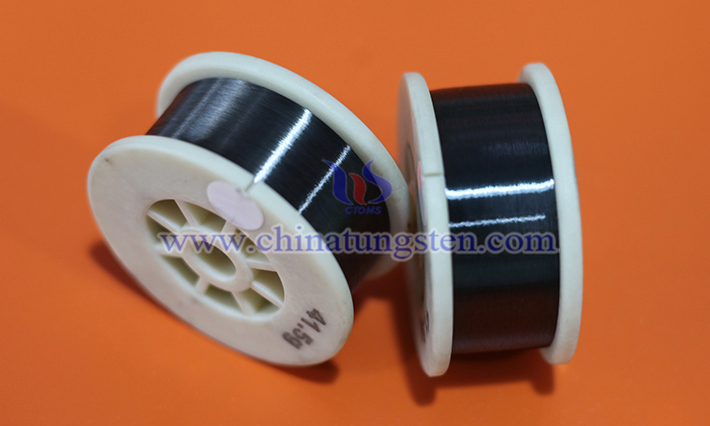

The applications of tungsten wire as reinforcement in composite materials primarily stem from its unique physical and chemical properties, offering significant advantages in composite systems requiring high strength, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, or special electromagnetic properties. Below is an analysis of its specific application scenarios and advantages:
Application of Tungsten Wire in Electron Tube Heaters
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 11 August 2025 19:15

The application of tungsten wire in electron tube heaters is primarily due to its high melting point, high resistivity, excellent thermal stability, and chemical inertness, making it an ideal material for the heated cathode (heater) in electron tubes.
Role of Tungsten Wire in High-Temperature Furnace Heating Materials
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 11 August 2025 19:14

Tungsten wire plays a crucial role in high-temperature furnace heating materials. Its high melting point, excellent electrical conductivity, chemical stability, and workability make it a core component for efficient and stable heating in high-temperature furnaces.
Tungsten Wire for Gas Discharge Lamp Electrode
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 11 August 2025 19:12

Gas discharge lamps, such as high-pressure mercury lamps and xenon lamps, play an important role in industrial lighting, stage lighting, automotive headlights, and other fields. As a key electrode material, tungsten wire is a core element in ensuring the stable and efficient operation of gas discharge lamps.
Tungsten Wire for Halogen Lamp Filaments
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 11 August 2025 19:10

Tungsten halogen lamps are highly efficient light sources that utilize tungsten as the filament. The reason for choosing tungsten as the filament is closely related to its unique physical and chemical properties.


 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com