What Are the Main Applications of Tungsten?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
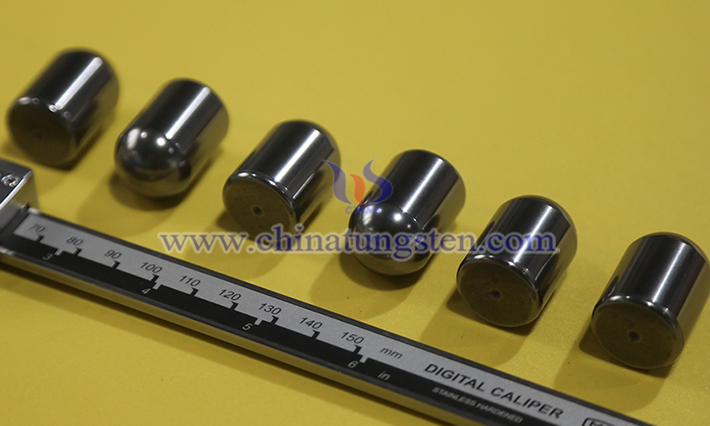

Tungsten is widely used in a variety of fields due to its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and high density. Tungsten's uses include:
What Is Tungsten?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
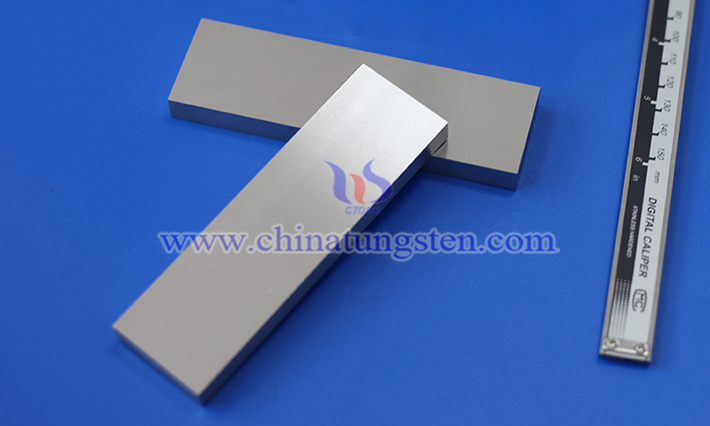
Tungsten is a silvery-gray transition metal with the element symbol W and atomic number 74. It has a high melting point (3422°C), high density (19.35 g/cm³), high hardness, and excellent high-temperature resistance. It is widely used in aerospace, defense, electronics, electric light sources, and cemented carbide.
Performance Comparison of Tungsten Resin and Lead
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
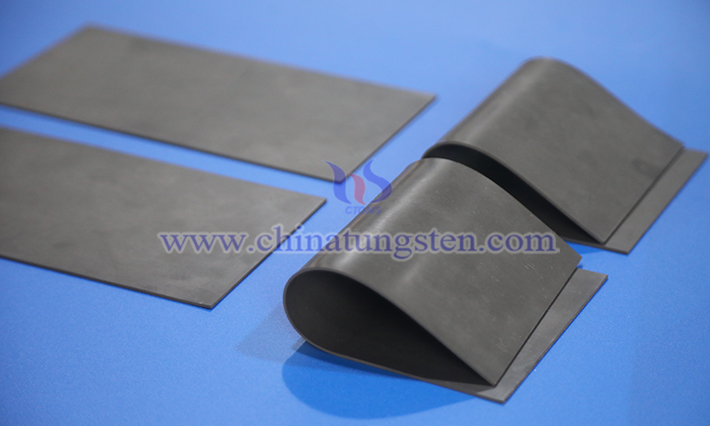
Tungsten resin is a composite material made from high-purity tungsten powder and polymer resin, renowned for its high density, eco-friendliness, and processing flexibility. Lead, as a traditional high-density material, has long been used in industrial, medical, and sports applications due to its low cost and good ductility. However, with growing concerns over environmental regulations and health safety, tungsten resin is increasingly replacing lead.
Applications of Tungsten Resin in Sports Equipment
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
Tungsten resin (Tungsten Resin) is a composite material made from high-purity tungsten powder combined with various resins (such as polypropylene, polyurethane, or thermoplastic materials).
Applications of Tungsten Resin in the Nuclear Industry
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
As an advanced composite material, tungsten resin is increasingly valued in the nuclear industry. This material combines the unique properties of tungsten with the flexibility of resin, forming an efficient and reliable solution suitable for nuclear environments requiring high protection and durability.
Applications of Tungsten Resin in the Medical Field
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
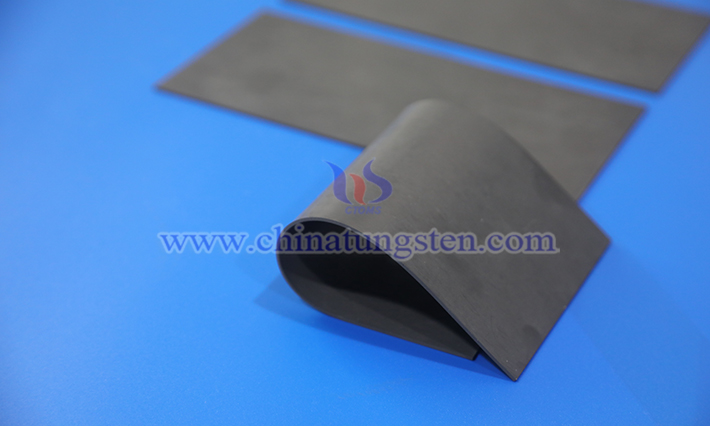
As a novel composite material, tungsten resin is increasingly widely used in the medical field. This material combines the excellent properties of tungsten with the flexibility and ease of processing of resin, creating an efficient and environmentally friendly solution.
What Are the Uses of Tungsten Resin?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
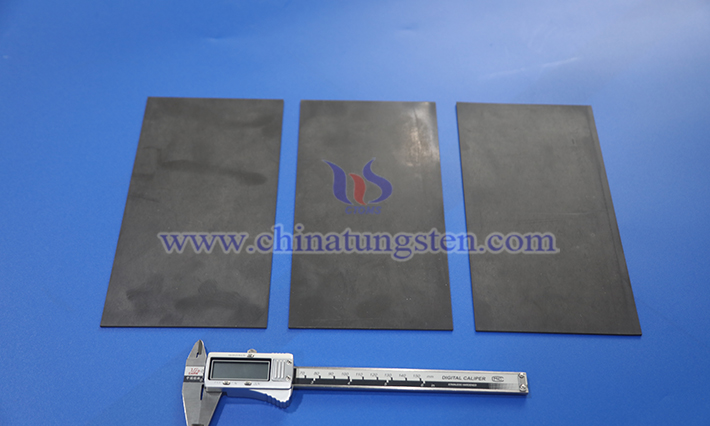
Tungsten resin, leveraging its high density, non-toxicity, radiation shielding capability, and processing flexibility, finds wide-ranging uses in medical, defense, industrial, civilian, and emerging technology fields.
What Are the Characteristics of Tungsten Resin?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
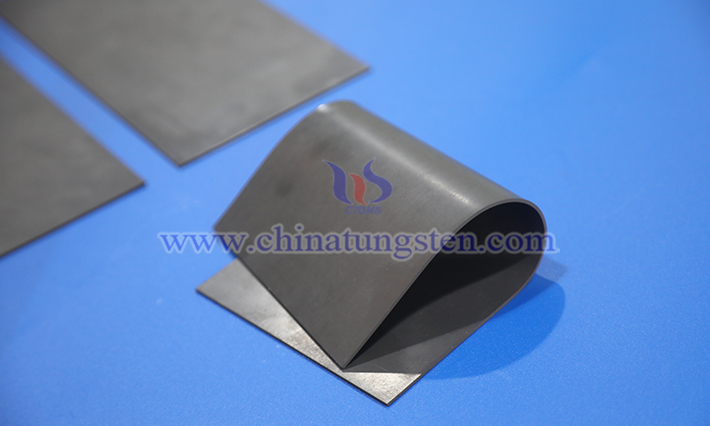
Tungsten resin is a composite material made by mixing high-purity tungsten powder with polymer resins (such as epoxy, polyurethane, or polyethylene). It is widely used in defense, medical, industrial, and environmental fields, thanks to its unique physical, chemical, and processing characteristics.
What Is Tungsten Resin?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
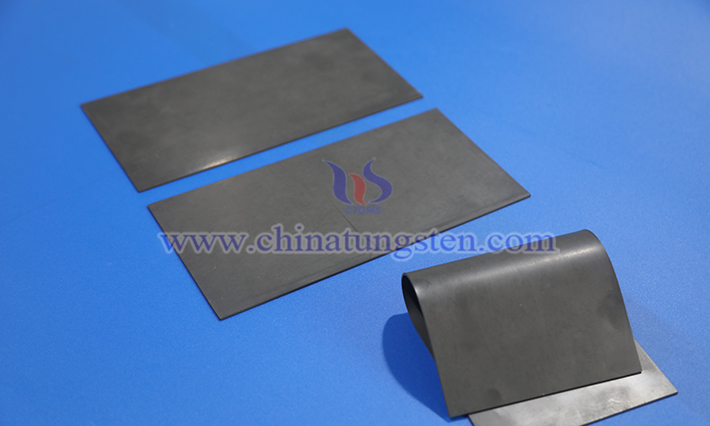
Tungsten resin, also known as tungsten polymer composite material or tungsten-filled resin, is a novel polymer composite material. It is primarily made by mixing high-purity tungsten powder with polymer resins (such as epoxy, polyurethane, or thermoplastic resins) in specific ratios and through specialized processes. This material combines the unique physical properties of tungsten (such as high density and radiation resistance) with the processing flexibility of resins, resulting in a non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and easily moldable material.
Application Fields of Tungsten Alloy Fasteners
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
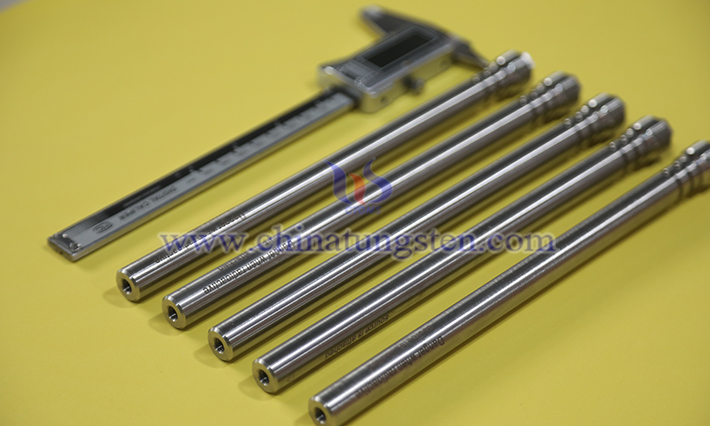

In contemporary industrial connection systems, tungsten alloy fasteners serve as high-performance connecting elements, playing a pivotal role and regarded as core components in materials engineering. Their exceptional performance stems from the inherent properties of tungsten and the optimization of other metal elements. Firstly, their high density ensures efficient weight distribution and connection stability within a limited volume.




 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com