Production of WO3 Nanoplates with Ammonium Paratungstate
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 18 November 2020 01:57
- Written by yuntao
- Hits: 2147
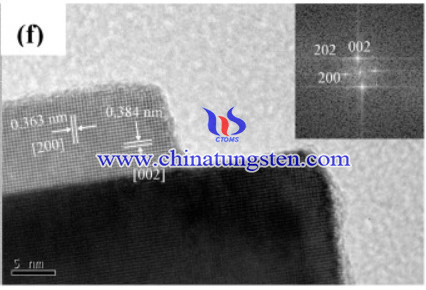
A fabrication process of tungsten oxide (WO3) nanoplates with ammonium paratungstate has been performed, the product showed great photocatalytic activity due to the plate-like shape.
Read more: Production of WO3 Nanoplates with Ammonium Paratungstate
Ammonium Paratungstate Applied in Production of Hexagonal Tungsten Trioxide Microspheres
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 18 November 2020 01:21
- Written by yuntao
- Hits: 1855
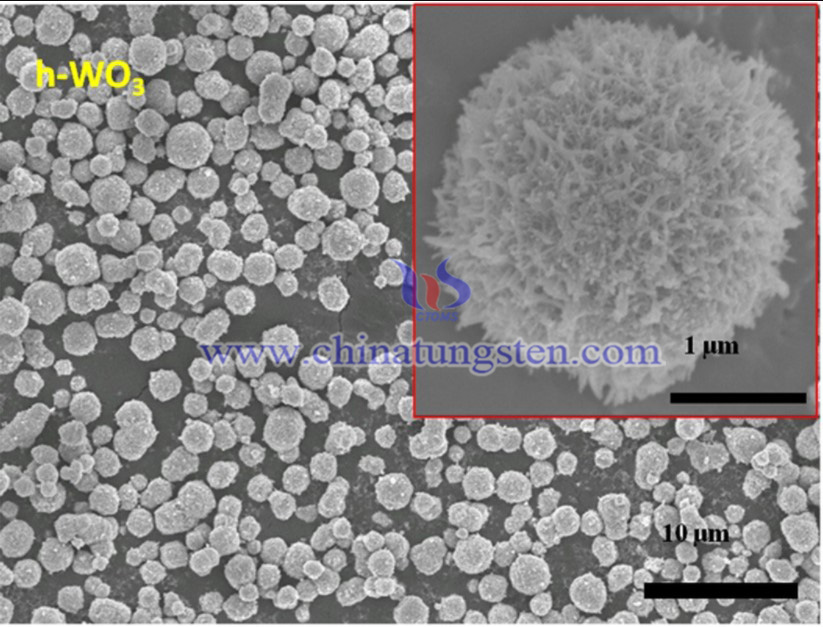
Ammonium paratungstate (APT) has been used as precursor material in production of Hexagonal tungsten trioxide (h-WO3) microspheres by hydrothermal synthesis. The as-prepared product showed significant catalytic activity in the hydrogenation of styrene under mild environment.
Read more: Ammonium Paratungstate Applied in Production of Hexagonal Tungsten Trioxide Microspheres
Ammonium Paratungstate in Synthesis of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 18 November 2020 01:11
- Written by yuntao
- Hits: 1764

Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) have been an area of intense research since their discovery in 1993, owing to their extraordinary mechanical and unique electronic properties. It has been applied in fields including field-emission, SPM tips, and sensors.
Read more: Ammonium Paratungstate in Synthesis of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
Ammonium Paratungstate Applied in WO3/Carbon Nanotubes
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 18 November 2020 01:21
- Written by yuntao
- Hits: 1807
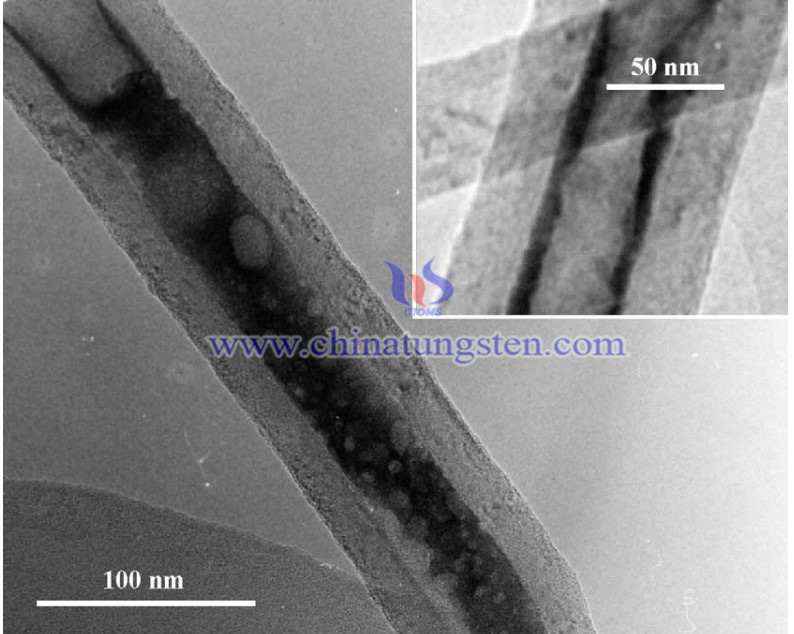

Solid acid catalysts play a significant part in chemical and petroleum industries in hydrocarbon conversion reactions required in octane enhancement processes, such as cracking, isomerization and alkylation, which can form highly branched isoparaffins. Such reactions need strong or moderate acid catalysts. However, halide-type solid acids have a great negative effect on environment. Tungsten oxides supported on oxide carriers have been considered as a more environmental-friendly substitute. Therefore, it has been well studied to be catalysts for hydrocarbon isomerization processes.
Read more: Ammonium Paratungstate Applied in WO3/Carbon Nanotubes
Comparison of Different Precursors for Tungsten Nanopowder Production—Tungsten, Tungsten Trioxide, Ammonium Paratungstate
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 18 November 2020 01:01
- Written by yuntao
- Hits: 1730

Tungsten nanopowder has been widely applied in industrial catalysis, hard materials, thermionic cathodes, and high-power batteries due to its highly oxophilic characteristics. tungsten is the hardest metal in the world, which makes it resistant to acids, alkalis, and oxygen.
More Articles...
- Effect Of Yttrium Barrier on Precursor (Y-Doped Ammonium Paratungstate) of WC-Co Cemented Carbide
- Production Of Nanostructured Tungsten-Lanthanum Oxide Composites Using Ammonium Paratungstate
- Chemical Vapor Synthesis (CVS) of Tungsten Nanopowder in Thermal Plasma Reactor Using Ammonium Partungstate
- A Large-Scale Production of Tungsten Trioxide Nanoparticles Using Ammonium Paratungstate





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com