Self-Passivating Tungsten Alloys and Surface Coating Protection Technology
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Tuesday, 02 May 2023 17:26
In order to solve the problem of poor oxidation resistance of W and W-based alloys at high temperatures, this work gives self-passivating tungsten alloys and surface coating protection technology. Optimization of the preparation process of the alloy (heat treatment of HIPed alloy, etc.) can effectively reduce or eliminate its internal cracks and holes, thermal stresses and residual stresses, thus reducing its surface roughness and porosity. In addition, some beneficial elements (Ti, Zr, Y, Nb, etc.) can be added to improve the high-temperature strength of W-based alloys, slow down the diffusion of Cr cations, and promote the formation of oxide films.
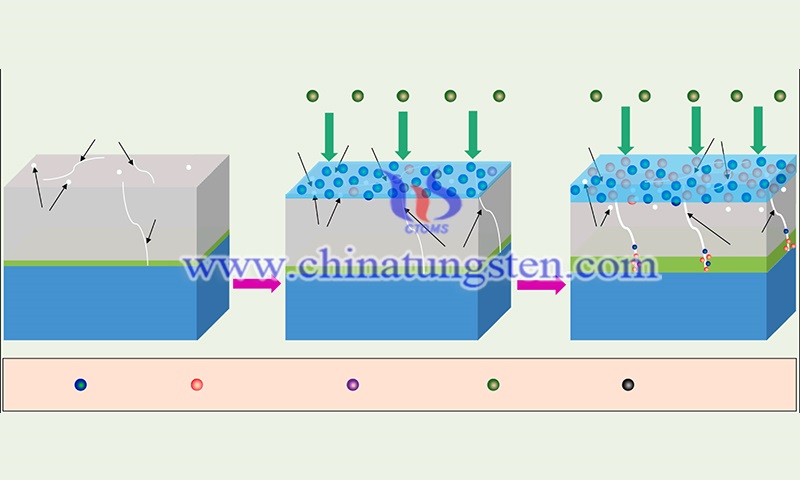
Studies have shown that tungsten-based alloys have good oxidation resistance at low temperatures (1000°C and below). However, the physical and chemical properties of tungsten alloys are influenced by the alloying to some extent. Therefore, the problem of poor oxidation resistance of tungsten alloys at medium and high temperatures (above 1000 °C) cannot be fundamentally solved. The silicide coatings prepared by surface coating technology have stable oxidation resistance at high temperatures (above 1300°C).
However, due to the CTE mismatch between the coating and the substrate, some cracks and holes will appear on the surface and inside of the coating. This will become a diffusion channel for oxygen to enter the coating and accelerate the oxidation of the coating. By appropriately increasing the thickness of the interfacial layer, the hazard of this problem can be mitigated to some extent. In addition, the two-step deposition process can make various elements complement each other in the diffusion process, and the coating structure can be further optimized.
Therefore, alloying combined with surface coating protection technology is a very promising protection method. It can not only improve the mechanical properties and medium-temperature oxidation resistance of tungsten alloys but also effectively improve the high-temperature oxidation resistance of tungsten alloys. Through the diffusion of alloying elements and coatings, the coating structure and composition can be optimized, and also the defects caused by the CTE mismatch between the coating and the substrate can be reduced, effectively improving the oxidation resistance of W-based materials. This requires a lot of further research work by subsequent researchers.
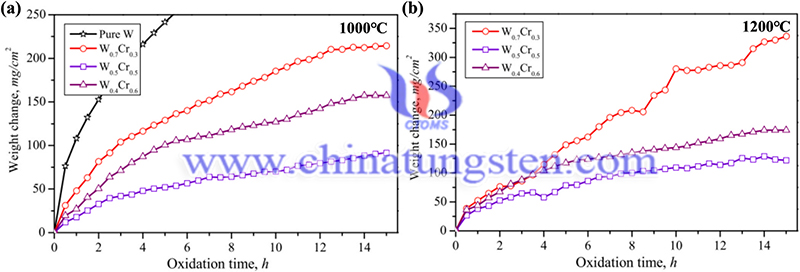
Reference: Fu T, Cui K, Zhang Y, et al. Oxidation protection of tungsten alloys for nuclear fusion applications: A comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 884: 161057.
- Tungsten Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com