2D MoS2/GOQD Nanocomposite Enables Ideal Humidity Sensor
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Friday, 29 April 2022 14:04
Research available as a pre-proof in the journal Materials Chemistry and Physics demonstrates the feasibility of using 2D molybdenum disulfide/graphene oxide quantum dot nanocomposites (2D MoS2/GOQD nanocomposite) as a sensing material for humidity sensor.
Humidity control and measurement are of great interest in a number of applications, such as the manufacture of electronic devices. The effectiveness of the humidity sensor depends heavily on the sensitivity of the sensing film. Two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials and metal oxide semiconductors are widely used as sensing membranes for humidity detection.
Among them, two-dimensional transition metal sulfides have gained prominence over other materials in the fabrication of sensors due to their high surface-to-volume ratio and excellent carrier mobility.

(Image Credit: PRO Stock Professional/Shutterstock.com)
Compared with other transition metal sulfides, MoS2 is more suitable for humidity detection. However, slow recovery/response time and low sensitivity are the main drawbacks of MoS2 sensing films, which must be addressed to improve the humidity detection performance of MoS2 film-based sensors.
Recently, several studies have shown that the humidity sensing performance of MoS2 sensors can be improved by modifying MoS2 films with metal oxides and metal nanocomposites. However, the modified MoS2-based sensors usually require higher operating temperatures, which increases the overall fabrication cost of the sensors.
The incorporation of graphene and its derivatives, such as GO, into MoS2 thin films, is increasingly becoming an effective way to improve the sensing performance of MoS2 sensors. For example, 2D MoS2/GOQD nanocomposite with high plasmonic conductivity has been successfully used to fabricate highly sensitive resistive sensors.
GOQD, which consists of some quantum-scale GO material fragments, is more suitable for humidity sensing applications compared to GO due to its large specific surface area and good hydrophilicity. In addition, the sensing membrane fabricated from GOQD possesses many inter-wafer voids, which facilitates the permeation process of water molecules within the moisture-sensitive membrane and accelerates the moisture-sensitive response of the sensor.
Therefore, MoS2/GOQD-based sensors made by combining GOQD and MoS2 have the potential to provide better performance in terms of sensitivity and response/recovery time. In this study, the researchers synthesized the first MoS2/GOQD composite film-based capacitive humidity sensor and investigated its humidity sensing performance.
Initially, interdigitated electrodes (IDEs) were prepared by a semiconductor fabrication process. First, a 400-nm-thick silicon dioxide layer was prepared on an N-type silicon wafer by thermal oxidation, and then a 300-nm/100-nm-thick gold/titanium layer was deposited on top of the silicon dioxide layer by magnetron sputtering. Gold electrodes with 20 μm wide gaps were fabricated by photolithography and wet etching. Before making the humidity-sensing film, it was cleaned with ethanol and deionized water in an ultrasonic cleaning device for 30 min and dried.
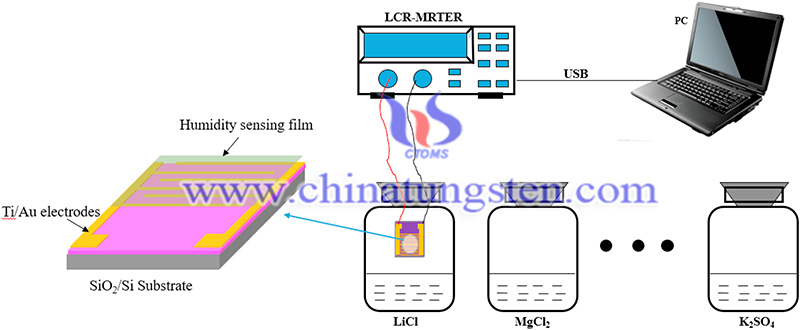
(Image Credit: Materials Chemistry and Physics)
MoS2/GOQD nanocomposite membranes were synthesized by a simple solution compounding method. Aqueous suspensions of GOQD and MoS2 were mixed in a fixed ratio and then sonicated for one hour to obtain the MoS2/GOQD composite suspension. Subsequently, a few drops of MoS2/GOQD suspension were applied to the gold IDE by micropipette drops and dried at 45 degrees C for 6 hours to obtain a moisture sensor based on the 2D MoS2/GOQD nanocomposite.
A humidity sensor based on MoS2/GOQD nanocomposite film was successfully fabricated. Elemental forms of sulfur, molybdenum, oxygen, and carbon were observed in the synthesized MoS2/GOQD composite film, indicating that the fabrication of the composite film was successful.
In the MoS2/GOQD composite membrane, GOQD and MoS2 are in close contact, which promotes carrier transfer and significantly facilitates the desorption and adsorption of water molecules.
The MoS2/GOQD film-based sensors show significantly higher responses to different RH levels. The sensitivity of the MoS2/GOQD composite film sensor is also considerably higher than 369 picofarads per RH compared to the pure GOQD and MoS2 sensors.
In addition, the sensors showed good long-term stability, fast response/recovery, low hysteresis, and good repeatability. In addition, the nanocomposite sensors fabricated in this study showed better sensing performance compared to previously reported humidity sensors, indicating the potential of these sensors in practical applications. In conclusion, the results show that 2D MoS2/GOQD nanocomposite can be an effective sensing material for manufacturing humidity sensors.
The study titled “High-sensitive humidity sensor based on MoS2/graphene oxide quantum dot nanocomposite” has been published in the journal Materials Chemistry and Physics on 20 April 2022. The study was carried out by the first author XiaoyuLi at the School of Chengdu Technological University, Chengdu, China.
| Molybdenum Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.molybdenum.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com