Graphene Intercalated Molybdenum Disulfide as Cathode for Zinc Batteries
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Sunday, 21 March 2021 17:26
Recently, the research group of Professor Xuanhui Qu of the University of Science and Technology Beijing has prepared graphene intercalated molybdenum disulfide nanosheets, which can be used as cathode materials for zinc batteries. It is not only increased the product capacity, but also effectively extends the service life of the battery.
Zinc battery owns the advantages of high theoretical capacity, low cost, environmental friendliness, and easy assembly. It is a large-scale energy storage system with great development prospects. However, strong electrostatic interaction between divalent zinc ion and host material, and the growth of zinc dendrites have restricted its applications.
At present, neutral or weakly acidic electrolytes have been proven to effectively improve the cycle stability of zinc anodes. Therefore, further development of the materials that match them and store zinc efficiently is the key to promoting the development of zinc batteries. Layered materials such as vanadium oxide and manganese oxide have been widely studied by virtue of the smooth two-dimensional zinc ion transport channel.
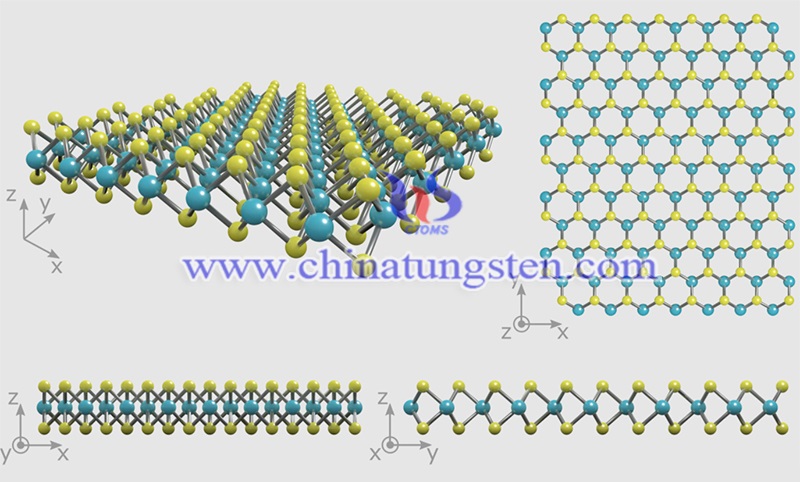
However, as a classic two-dimensional layered transition metal sulfide, molybdenum disulfide is rarely used for zinc storage. This is mainly due to the small interlayer spacing (0.62 nm) and poor hydrophilicity of bulk MoS2 limits. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop MoS2-based zinc storage cathode materials with larger interlayer spacing and good hydrophilicity.
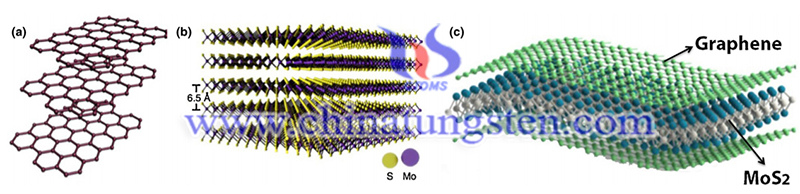
To solve the issues, researchers of Beijing University of Science and Technology adopted an electrostatic self-assembly strategy to successfully insert graphene between MoS2 layers. The MoS2 layer spacing was significantly expanded from 0.62nm to 1.16nm, and the reduced graphene oxide and 1T-rich MoS2 gave the material better electronic conductivity and hydrophilicity.
The prepared graphene intercalated molybdenum disulfide composite "sandwich" structure is self-assembled into a flower-like structure, which effectively inhibits the stacking of MoS2 layers and graphene layers. Compared with bulk MoS2, the composite material can increase zinc storage capacity by more than 10 times, and has better cycle stability (capacity retention is about 88.2% after 1800 cycles).
Studies have shown that the composite material has a higher zinc ion diffusion coefficient and a lower ion migration energy barrier. Moreover, the graphene intercalated molybdenum disulfide cathode, and zinc foil electrode were matched to assemble quasi-solid zinc batteries, which demonstrated excellent cycle stability and flexibility.
| Molybdenum Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.molybdenum.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |