What Kind of Crystal Is Tungsten Diiodide?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 14 June 2023 17:20
Tungsten diiodide is a transition crystal. Transitional crystals are different from many substances in nature with regular geometrical shapes, such as ionic crystals, molecular crystals, atomic crystals, and metal crystals. The inter-particle role of the lattice junctions of the transitional crystals has changed, and the interactions between particles of the crystalline structure and the nature of the crystal between the different types of crystalline forms, which is difficult to be classified as any of the above-mentioned typical crystals, and there are a lot of actual crystals belonging to the transitional crystals.

The concept of electronegativity was introduced in chemistry to further the judgment of ionic, transition, and molecular crystals and bonding, and to further understand the physical properties of substances, such as melting and boiling points.
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom of an element to attract electrons to its side in a molecule. Electronegativity is not a property of an isolated atom, but of atoms in a molecule under the influence of surrounding atoms. There are many different electronegativity scales and different data, but the change in electronegativity in the Periodic Table is consistent. In the same period, from left to right, the electronegativity increases (except for rare gases), the non-metallicity of the element increases, and the metallicity decreases; in the same main group, from top to bottom, the electronegativity decreases, the non-metallicity of the element decreases, and the metallicity increases. The electronegativity of the transition elements does not change significantly; they are all metals, but they are not as metallic as the elements of the first (IA) and second (IIA) main groups.
Electronegativity can be a comprehensive measure of the metallic and non-metallic properties of various elements. In the case of iodine and tungsten contained in tungsten diiodide itself, tungsten is a transitional metallic element with an electronegativity of 1.7, while iodine is a non-metallic element with an electronegativity of 2.5. As we can see, iodine's electronegativity is greater than tungsten's, which means that iodine's atoms have a stronger ability to attract electrons than tungsten's, and are more inclined to produce anions.
As a transition crystal, the electronegativity of iodine and tungsten in tungsten diiodide is weaker than that of ionic crystals and stronger than that of covalent crystals. Therefore, the transition from ionic crystals to molecular crystals is present, and the melting and boiling points are lower than those of ionic crystals but higher than those of molecular crystals.
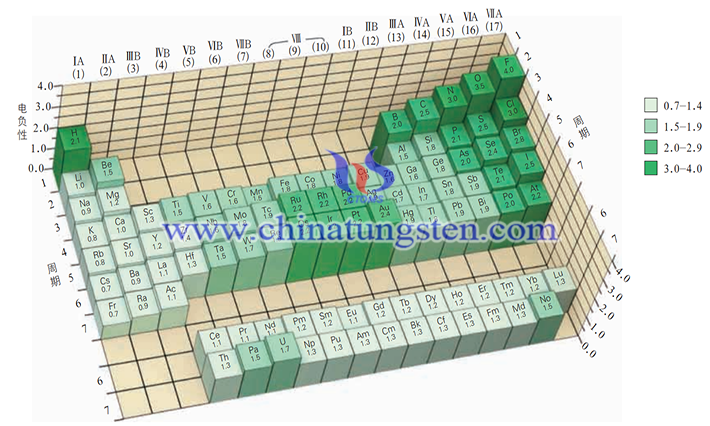
Tungsten diiodide is a kind of transition-type crystal that needs to introduce electronegativity to judge the physical properties due to the variation of inter-particle interaction in the lattice junction.
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com