Tungsten Disulfide for Laser Saturable Absorbers Application
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 15 September 2022 21:55
The researchers found that tungsten disulfide (WS2) can be converted into a direct semiconductor with a band gap of 2.1 eV by controlling the chemical composition and number of layers due to the quantum confinement effect. In addition, WS2 has better saturable absorption properties than graphene and carbon nanotubes in the near- and mid-infrared bands. Due to these excellent properties, it is increasingly being used in laser saturable absorbers (SAs).
(Photo source: Liu et al./Optics Express)
Compared with conventional lasers (such as solid-state lasers, gas lasers, and semiconductor lasers), fiber lasers have inherent advantages, such as good beam quality, high environmental stability, high optical-to-optical conversion efficiency, good durability, and good heat dissipation performance. Fiber lasers have been widely used in surgical procedures, nonlinear frequency conversion processes, and optical infrared oscillator pump sources.
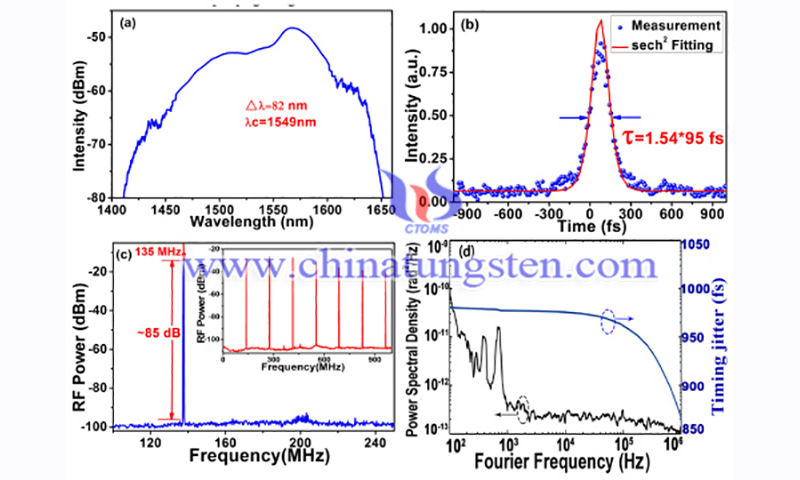
In 2015, Wu et al. prepared a small amount of monolayer WS2 dispersions and then embedded WS2 nanosheets in polyvinyl alcohol films as SA for fiber lasers. They achieved both Q-switching and mode-locking of the fiber laser. The researchers mainly used WS2 to obtain a high-energy Q-switched fiber laser because of its high damage threshold and large modulation depth when used as laser saturable absorbers.
For example, a Q-switched pulse with a pulse energy of 195 nJ was obtained in the 1.5 µm band with the WS2 SA. State-of-the-art fiber lasers using tungsten disulfide SA generate pulses in the 1 µm, 1.5 µm, 2 µm, and 2.865 µm bands by Q-switching and mode-locking. In particular, Wei et al. proposed the use of WS2 as SA in a co-doped fiber laser for passive Q-switching in the 2.865 µm band. They obtained a maximum output power and pulse energy of 48.4 mW and 0.42 µJ, respectively, which are much higher than previously reported WS2-based pulses at other wavelengths. Most of the previously mentioned WS2 films were formed by physical deposition.
(Photo source: Liu et al./Optics Express)
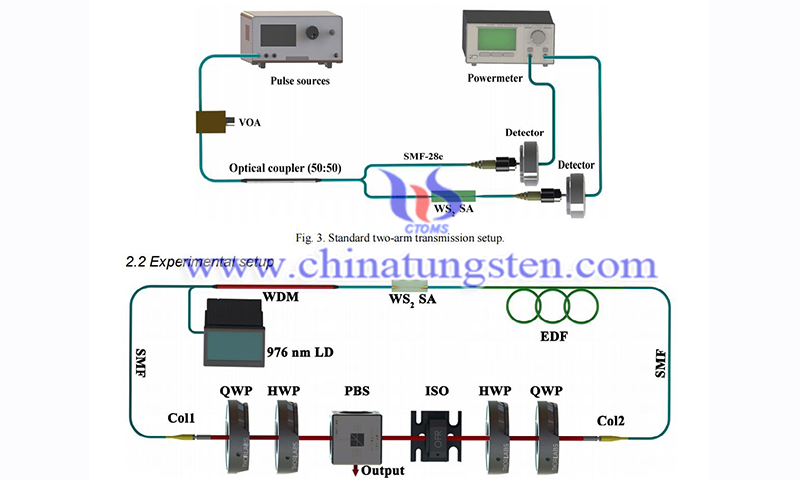
Yang et al. used CVD to prepare WS2 thin films as laser saturable absorbers materials for mode-locked all-fiber lasers and showed experimentally that monolayer WS2 is a new type of SA that can be used to achieve Q-switched pulses at the microsecond level or mode-locked pulses at the nanosecond level. So far, the saturable absorption properties of WS2 have been extensively studied and applied in fiber lasers.
Cited Article: Ding J, Feng A, Li X, et al. Properties, preparation, and application of tungsten disulfide: A review [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2021, 54 (17): 173002.
- Tungsten Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com