Annealing Effect on Tungsten Bronze Niobate Dielectric Properties
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 16 May 2016 18:33
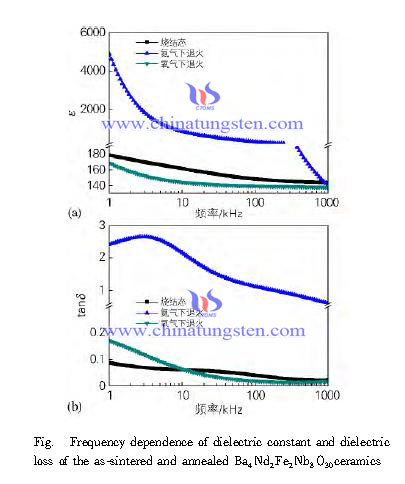
Dielectric constant and loss changes with frequency of both unannealed and annealed Ba4Nd2Fe2Nb8O30 ceramics is shown in Fig. The dielectric constant of all samples increase with frequency decreases, which is due to the low frequency, there area variety of different mechanisms of polarization like electron polarization, ionic polarization, dipole orientation polarization, space charge polarization and spontaneous polarization in niobate ferroelectric, while as the frequency rises, some of the slow polarization mechanisms such as space charge polarization will be gradually too late to reverse, leading to its disappearance, thus reducing the dielectric constant.
When the frequency changes from 1kHz to 1MHz, the relative dielectric constant ε of Ba4Nd2Fe2Nb8O30 ceramic without annealing treatment is reduced from 179 to 143, the dielectric loss tanδ reduced from 0.088 to 0.021. When Ba4Nd2Fe2Nb8O30 ceramics annealing in the oxygen atmosphere, there is a similar variation, the relative permittivity ε reduced from 168 to 137, the dielectric loss tanδ reduced from 0.17 to 0.016.
However, compared with the unannealed situation, Ba4Nd2Fe2Nb8O30 ceramic annealed in the nitrogen atmosphere, the relative dielectric constant increases rapidly from 179 to 5000 (1kHz). When the frequency changes from 1kHz to 1MHz, the relative dielectric constant quickly dropped from 5000 to 140. Over the entire frequency range, dielectric loss tanδ has always been huge, when the frequency at 1kHz to 10kHz, there has been a loss peak. This phenomenon is typical spatial charge polarization. After the annealing treatment in the nitrogen atmosphere, the oxygen vacancies of Ba4Nd2Fe2Nb8O30 ceramic increased significantly, resulting in conductivity ceramics decreased, thereby greatly enhancing the space of charge polarization, resulting in dielectric constant surge, and dielectric loss peak appeared at the corresponding frequency. The changes of dielectric properties indicates that the oxygen vacancies have a significant impact on dielectric properties of tungsten bronze niobate ceramics.

| Tungsten Oxide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.tungsten-oxide.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |