CsxWO3 Powder Concentration Effect Experiment
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 28 March 2016 17:12
Synthesizing of homogenous CsxWO3 powder, Cs2CO3 of various concentration and H8MoN2O4 were mixed in aqueous, dried at 180 ℃ for 8 hr. The precursor as dried at 180 ℃ was heated in a tubular furnace at 450 ℃ for 1 hr with H2/N2 gas flow at H2/N2=90/10, followed by annealing at 800 ℃ in an N2 gas for 0.5 hr. The as-produced powders were dispersed by turbomill with iron ball for 2hr and the zirconia bead for 1 hr respectively. In the other hand, nanocomposite films were prepared with mixing urethane acrylic/UV coating binder and well dispersed perovskites sol by using bar coater. Dispersion and coating binder were mixed well in vial with rotating mixer. The prepared films were dried at 80 ℃ for 1min in heating chamber and illuminated with a mercury UV lamp UV-curing equipment at intensity 800 W/cm for 20 sec. The structure and sizes of synthesized perovskite particles was observed XRD and PSA spectrometer, the optical properties of their composite films were investigated by UV-VIS and NIR spectrometer. The synthesis of products is summarized outlined in Scheme1.
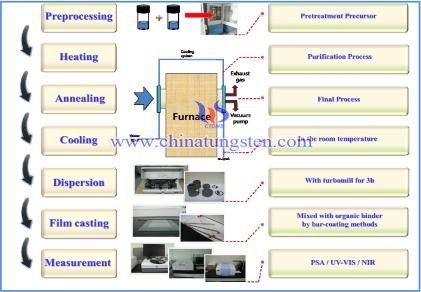

Scheme 1. Synthetic scheme of the nanoparticles and theirs composite films.
X-ray crystallography is a tool used for identifying the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline atoms cause a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their disorder and various other information.
X-ray crystallography is a tool used for identifying the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline atoms cause a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their disorder and various other information.
| Tungsten Oxide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.tungsten-oxide.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com