Crystal Structures of Tungsten Disulfide and Tungsten Diselenide
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 22 August 2022 20:33
An article published in the Journal of Solid State Chemistry by Schutte et al. illustrates that crystal structures of tungsten disulfide (WS2) and tungsten diselenide (WSe2) host the same type of layered structure as molybdenum disulfide (MoS2). In addition to the common hexagonal 2H form of WS2, a rhombohedral form, 3R-WS2, has also been reported, which is isotypic to the rhombohedral form of MoS2.
In addition to the rough determination of the atomic positions of 2H-WS2 and WSe2 from powder X-ray diffraction data, the atomic positions must be accurately known in order to calculate the electronic structure of these compounds.
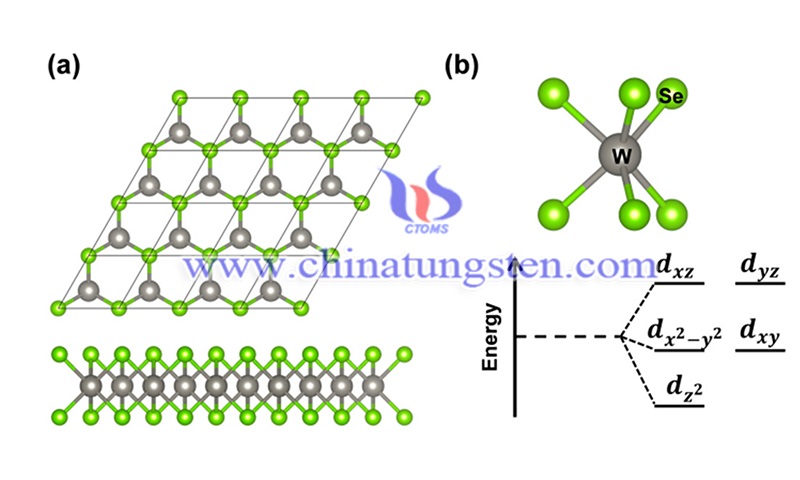
(Picture source: Liu et al./Nanomaterials)
The researchers prepared single crystals of tungsten dichloride by chemical transport using chlorine (2H-WS2) or bromine (3R-WS2, WSe2) as the transport agent. Very thin platelet crystals were studied by X-ray diffraction using a Nonius CAD4 diffractometer; monochromatic MoKa radiation was used. The single-crystal parameters were determined by least-squares fitting of optimized setup angles for about 20 reflections in the ranges of 20-24° (2H-WS2), 30-35° (WSe2), and 27-31°.
A modified version of the CAD4 program was used to measure each reflection of a thin plate-like crystal at its minimum absorption position. The intensity of the equivalent reflections was averaged and corrected for Lorentzian and polarization effects.
In this study, the full matrix least squares method was used in the refinement process. The atomic scattering coefficients are the scattering coefficients of the XTAL system and the anomalous dispersion coefficients are taken from the "International Tables for X-Ray Crystallography". The results confirm that 2H-WS2 and WSe2 are isomorphic to 2H-MoS2 and have space group P63/mmc. The scattering coefficient of sulfur is relatively small compared to that of tungsten. The trigonal prisms formed by the brass atoms around the tungsten atoms are quite regular.
In contrast, in NbS2, NbSe2, and TaSe2, the metals have a d1 configuration with shorter prismatic edges parallel to c than those perpendicular to c. It can be said that the trigonal coordination is stable only for metals with d0, d1, or nd2 (n > 3) configurations. In the semiconducting molybdenum and tungsten dicarbides, the interlayer distances X-3X is much longer than the X-X distances within the layers; in the metallic niobium and tantalum dicarbides, this difference is smaller.
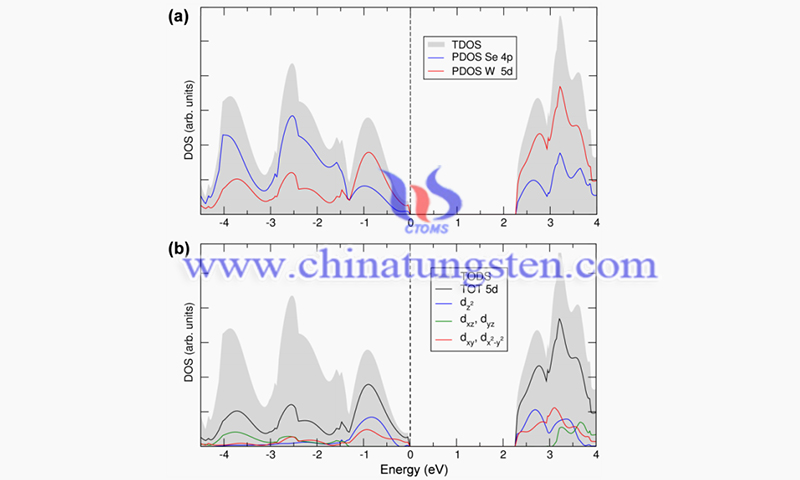
(Picture source: Liu et al./Nanomaterials)
Article Source: Schutte W J, De Boer J L, Jellinek F. Crystal structures of tungsten disulfide and tungsten diselenide [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1987, 70(2): 207-209.
- Tungsten Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com