Synthesis Of Nonmagnetic Ni(W) Using Ammonium Paratungstate And Nickel Powder
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 09 September 2020 11:08
To ensure the electromagnetic characteristics and processing quality and efficiency of cutting magnetic components, the properties of nonmagnetic and good wear residence of Forming die and cutting tool are the major factors.
The magnetism of hard tool materials commonly comes from Co, Ni and Fe, which is binder material. In order to realize no magnetization of the hard tool materials, nickel based nonmagnetic solid solution powder is worthy of serious thought for binder of hard tool material. And from Ni-W binary diagram, it can be seen that the maximum solubility content of W in Ni is 31 wt.%, and when the W solubility content in Ni is more than 18 wt.%,the magnetic transition temperature of nickel is reduced to room temperature and the Ni-W solid solution becomes non-magnetic.

Owing to their superior mechanical, electrical and corrosion resistance properties compared to Ni, Ni-W alloys are attractive as potential candidates for quite a number of industrial applications such as environmentally friendly substitutes for hard chrome plating, substrate for high temperature superconductors and catalysts for hydrogen evolution from alkaline solutions
nickel powder and ammonium paratungstate (APT) are applied as the precursor of the mechanical alloying method. APT is the starting material for preparation of tungsten powders, and by controlling the decomposition condition of APT, ultrafine tungsten powder can be produced. The decomposition of APT should be conducive to the mutual diffusion between Ni and W. From this point of view, nonmagnetic Ni(W) solid solution powders were manufactured by mechanical alloying and diffusion of Ni and APT powders.
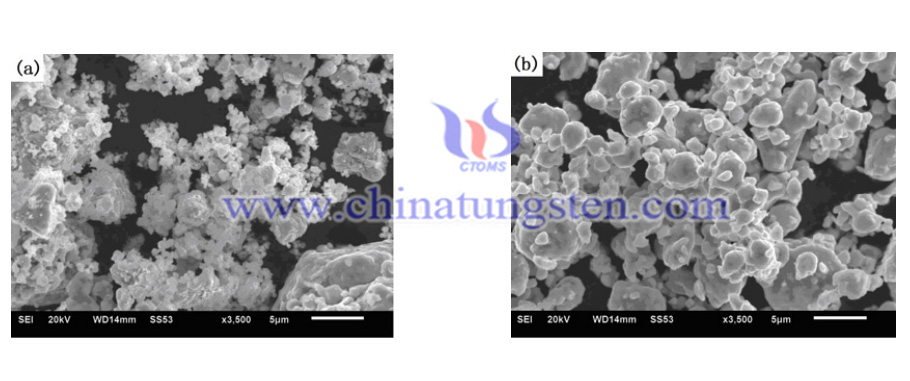
The exact procedures are as follows:
- The Ni(W) solid solutions were manufuctured by using APT and pure tungsten powder. Nickel (99.9%) and APT (99% purity) powders were mixed to constitute powder blends with APT contents of 30.0 wt.% (convert to 20 wt.% W).
- Blended mixtures were mechanically alloyed (MA’d) for 48 h using a XQM series planetary ball mill with a speed of 360 rpm with WC-Co balls and the ball-to-powder weight ratio was 7:1. Diffusion of Ni-APT powders were conducted at 550 °C for 2 h and then 800 °C for 2 h under H2 atmosphere.
- For the sample without using APT, nickel (99.9%, 36 μm) and W (99.9%, 18 μm) powders were mixed to constitute powder blends with the composition of 80 wt.% Ni and 20 wt.% W. The condition of mechanical alloying of the Ni-W powder blend is the same as that of the Ni-APT powders. Diffusion of the powder was conducted at 800 °C for 2 h under H2 atmosphere.
- The shapes and sizes of the diffused powders were conducted using a JSM-7001F Thermal Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). The phases of the as-MA’d and diffused powders were examined by Smartlab Polycrystalline X-ray diffractometer (XRD) (Cu Kα radiation). W solubility amounts in the Ni lattice of Ni(W) solid solution were calculated by using the formula (1) of Vegard’s law with XRD peak (111) diffraction angle of the Ni(W) phase. XW = −7.5208 + 2.13429ANi-W (1) where XW is the atomic fraction of W in Ni, and ANi-W is the lattice parameter Magnetic saturation of the diffused powders were determined using Lake Shore (VSM). The system was calibrated using pure nickel references. The test piece of the powder was weighed and inserted into a non-magnetic holder. The external magnetic field intensity was 4000 G. Each measurement was repeated twice to check consistency of results.
In conclusion. Nonmagnetic Ni(W) solid solution powders were fabricated using Ni and ammonium paratungstate (APT) powders via mechanical alloying and diffusion. Independent of manufacture conditions, the magnetic saturations (Ms) of Ni(W) solid solution powders derived from APT as the tungsten source were lower than that from W powder. The powders prepared using APT as the tungsten source have higher activity and finer particle size, which is conducive to the mutual diffusion between Ni and W, resulting in a faster solid phase reaction and the amount of W dissolved in Ni is higher. The obtained Ni(W) solid solution powders are nearly zero magnetism.
- APT Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: ammonium-paratungstate.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com