How to Solve the Problem of "Coarsening" of Ultrafine Tungsten Carbide Powder
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 06 February 2019 21:33
Ultrafine cemented carbide has the advantages of high hardness, high strength and good toughness. It is called "double-high" cemented carbide, and is widely used in high-efficiency precision tools, micro-drills, micro-milling, blades, precision molds and so on.
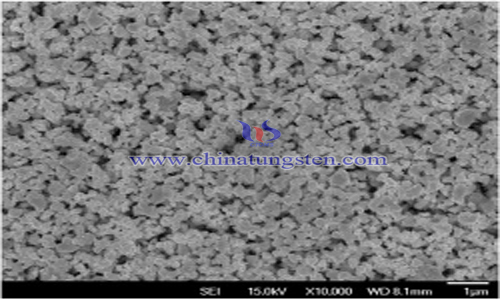
However, due to the coarse grain size of tungsten dioxide, generally between 10-50 micron, some of the aggregates will be retained in the reduction and carbonization process, forming ultrafine tungsten carbide aggregates, whose particle size is between 1-10 micron. Even if these aggregates are fragmented and dispersed, they will preferentially dissolve in the cobalt phase during the liquid phase sintering stage of the subsequent alloy preparation, and precipitate on other coarse grains, forming abnormally long coarse grains (commonly known as "coarsening"), affecting the properties of the alloy.
In order to solve the problem of "coarse", researchers have designed a method of preparing ultrafine tungsten carbide powder by oxidation-reduction method. The ultrafine WO3 powder is obtained from tungsten dioxide powder by oxidation-calcination and hydrogen reduction. The ultrafine tungsten carbide powder is obtained by carbon blending, carbonization, ball milling and sieving.
1.The calciner is heated to 800 ℃, and compressed air is introduced. The tungsten dioxide powder is oxidized and calcined in the calciner for 4 hours. The calcined WO3 powder is screened to remove iron impurities, and the phase composition and Feldspar particle size are tested.
2.WO3 powder was reduced in a reduction furnace at H2 atmosphere and 650 ℃ for 8 hours. The reduced tungsten powder was sieved to remove iron impurities, and the oxygen content and BET particle size were measured. The mixture of tungsten powder and carbon black is milled in a ball mill for 6 hours, then the mixture of W+C is carbonized in a carburizing furnace. The carbonization atmosphere is H2 atmosphere, the carbonization temperature is 1100 ℃, and the carbonization time is 6 h. The carbonized powder is milled in a ball mill for 5 h. After ball milling, the material is separated by 12-mesh sieve, and then by 120-mesh sieve to remove the undisturbed material. Ultrafine tungsten carbide powder was obtained after sieving with impurities.
Using chemical reaction and phase transformation in the oxidation process of tungsten dioxide, through chemical energy, the powder can be broken and dispersed from inside to outside, and the ultrafine WO3 with finer particle size, better dispersibility, uniform particle size distribution and no aggregates can be obtained. Compared with the traditional physical crushing, the chemical force is used to crush the powder, and the activation energy of the powder surface is not increased after crushing, at the same time, the powder in the crushing process is avoided. The adsorption of water in air after crushing is beneficial to the control of particle size and properties of tungsten powder in the subsequent reduction process, and to ensure the stability of the quality of tungsten powder, so as to prepare ultrafine tungsten carbide with small particle size, good dispersion and uniformity.
- Tungsten Powder Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-powder.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com