How to Prepare Porous Silicon / Multidimensional Tungsten Oxide Composites
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 02 February 2019 22:57
Tungsten oxide, as a semiconductor sensitive material with great research and application prospects, has been widely used to detect various toxic and dangerous gases (such as NO2, NH3, etc.). However, the working temperature of tungsten oxide is relatively high (150 ~250 ℃), so scientists and technicians have been devoting themselves to the research of reducing the working temperature of tungsten oxide.
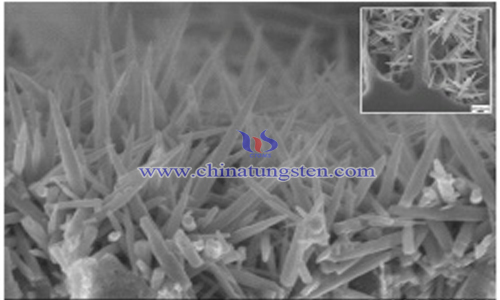
Correspondingly, porous silicon is a new gas-sensing material with adjustable pore size, depth and porosity formed by corrosion on the surface of silicon wafer. It can be used to detect NOX gas at room temperature. However, porous silicon also has the disadvantage of low sensitivity, which will restrict its practical application.
The process of porous silicon matrix compounding with tungsten oxide by some researchers includes the following steps:
(1) Preparation of Porous Silicon
Porous silicon layer was prepared on polished surface of step (1) by double cell electrochemical etching. The electrolyte consisted of hydrofluoric acid with 40% mass concentration and dimethylformamide with 40% mass concentration. The volume ratio was 1:2. The applied current density was 64 mA/cm2 at room temperature and without illumination. The etching time was 8 minutes, and the formation area of porous silicon was 1.6 cm x 0.4 cm. The average pore size of porous silicon is 1.5 micron and the thickness of porous silicon layer is 19 micron.
(2) Preparation of seed layer
1.65g sodium tungstate was dissolved in 100 ml deionized water by magnetic stirrer, then dilute hydrochloric acid was added drop by drop until no white precipitation was produced. Then the mixed solution was placed for 1 h. The seed solution was rotated on the porous silicon prepared in step (2), rotated for 5 layers, and then heat-treated in muffle furnace. The heat-treated temperature of the seed layer was 650 ℃. The heating rate is 2.5 C/min and the interval is 2 h.
(3) Gas Sensor with Porous Silicon-based Tungsten Oxide Nanorods Composite Structure Prepared by Hydrothermal Method
Firstly, the reaction liquid is allocated, and 4.13g sodium tungstate is weighed. It is dissolved in 12.5ml deionized water by magnetic stirrer. Then, the pH value of the reaction liquid is adjusted to 2.0 by dilute hydrochloric acid. Then, the above solution is diluted to 125 ml, and oxalic acid is added to control the pH value of the solution to 2.5. Then, 70 ml of the reaction liquid is transferred to the PTFE lining of 100 ml hydrothermal reactor. Then, the porous silicon substrate with seed layer was inserted on the sample rack and placed horizontally in the lining. Finally, the reactor was placed in the constant temperature drying chamber and reacted at 180 ℃ for 2 hours.
(4)Cleaning of porous silicon substrates after hydrothermal reaction
The porous silicon wafers after hydrothermal reaction were soaked repeatedly in deionized water and anhydrous ethanol, and then dried in a vacuum drying chamber at 80 ℃ for 10 hours. The porous silicon-based multi-dimensional tungsten oxide composite structures with different morphologies were prepared. The results of electron microscopy analysis show that there are a large number of one-dimensional tungsten oxide nanorods at the bottom of the porous silicon hole. The average diameter of the nanorods is 50 nm and the length is 900 nm.
The porous silicon / multidimensional tungsten oxide composites have high specific surface area. Meanwhile, ordered tungsten oxide nanorod arrays are more conducive to gas adsorption and free diffusion. This material has important practical significance in reducing the working temperature of gas sensors, improving the sensitivity and selectivity of sensors. Practice and research value.
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com