Tungsten Oxide Ceramics EDS Spectroscopy
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 12 March 2018 10:29
The leakage current of the tungsten oxide ceramic varistor under the action of the applied voltage is a decreasing process with time. This shows that the grain boundary barrier model of tungsten oxide varistors is different from conventional varistors such as zinc oxide.
For a typical zinc oxide varistor, the leakage current will increase with the loading time under a certain voltage. Its electrical energy consumption increases, the sample temperature increases, and finally thermal breakdown. The reason for the aging of zinc oxide varistors is that at certain voltages, the interstitial ions of the depletion layer move into the grain boundaries and negative electron defects at the grain boundaries. At the same time, the desorption of the oxygen anion at the grain boundary leads to a full decrease of the grain boundary potential barrier. As a result, the grain boundary resistance decreases, the leakage current increases, Joule heating occurs, and the grain boundary barrier is further reduced.
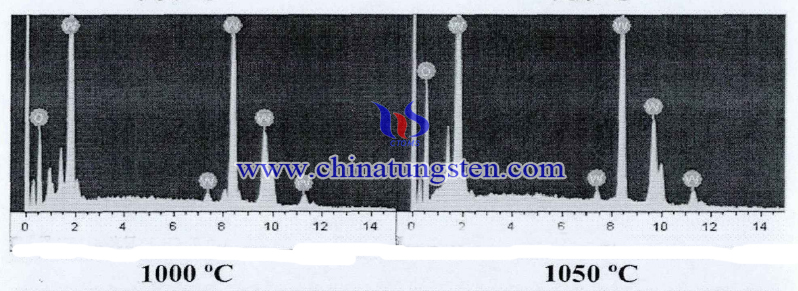
Since tungsten oxide is an N-type semiconductor mainly composed of oxygen vacancies, there are oxygen vacancies inside the crystal grains. That is, the ratio of the number of oxygen atoms in the crystal grains to the number of tungsten atoms is less than 3. The surface of the tungsten oxide ceramic grains is oxygen-rich, that is, the ratio of the number of oxygen atoms in the surface of the crystal grains to the number of tungsten atoms is greater than 3. Analysis of the elemental content of the grain surface of the sintered sample confirmed that the ratio of oxygen atoms to the number of crane atoms on the surface of crystal grains was greater than 3.
The figure is a spot-scanned EDS pattern of the grain surface of the sample sintered at different soak temperatures. As the holding temperature increases, the peak of oxygen increases. The peak value of the oxygen element of the tungsten oxide ceramic sintered at 1050°C is the highest. The ratio of the oxygen atom to the crane atom is greater than 3. It is indicated that the oxygen enrichment process on the grain surface occurs in the cooling process during sintering of the tungsten oxide ceramic.

- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com