Composition Changes of WC-Co Tungsten Carbide
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 02 March 2018 21:21
WC-Co tungsten carbide is a kind of widely used tungsten carbide, of which the sintering theory is the most mature and perfect. The composition of WC-Co tungsten carbide will change with the change of temperature during sintering. These changes have both the phase change and the chemical change of the eutectic reaction.
For the sintering of tungsten carbide, the control of the heating stage is very important. It is necessary to fully understand the composition changes during the heating process.
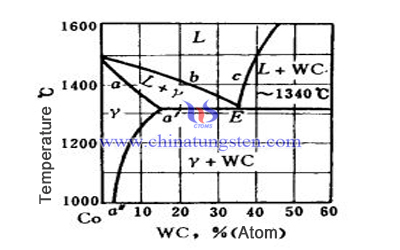
1, Presintering and Before the Temperature Rises to Eutectic Temperature
This process is a kind of solid phase sintering process. When the temperature is over 500℃, the sintering between Co particles and between the Co and WC particles is started, thus increasing the strength of the blank. At 1000℃, WC begins to diffuse to solid solution in the Co phase and accelerated with the increase of temperature. The content of WC in Co-WC solid solution (γ phase) increased along the a'a'' line. And the eutectic temperature reached the maximum.
2, Eutectic Temperature
When the temperature continues to rise to the eutectic temperature, the inverse reaction of the eutectic reaction between the γ phase and WC occurs, producing the liquid phase. If the system is fully balanced at this time, all of the γ phase will enter the liquid phase, but there are still a large number of WC solid phase.
3, Heating Up to Sintering Temperature (Maximum Temperature)
More WC dissolves into the liquid phase that the volume of the liquid phase increases dramatically. When the components of the liquid phase change along the Ec line and reach the C point (the sintering temperature), the system tends to balance. A part of the cobalt is not converted into gamma phase during the heating process, the components of the γ phase cannot reach the a' point at the eutectic temperature.
As not all can be transferred to the liquid phase. Then the remaining part of the γ phase will continue to dissolve WC when it exceeds the eutectic point and transform into liquid phase, of which the components will change along the Eb line.
In this way, when the sintering temperature is reached, the average component of the whole liquid phase is not a point of c, but a point between b and c. At the same time, there may still be a part of gamma solid solution with WC content less than a 'point. This part of the γ phase can also continue to dissolve WC in the heat preservation stage, so that the components change along ab, and then change to liquid phase after reaching b point.
- Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com