Sintering: Evaporation - Condensation
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Sunday, 25 February 2018 18:21
In the sintering process of tungsten carbide, material migration is usually accompanied. At high temperature, the phenomenon of material evaporation from particle surface to space may also occur during sintering, which has a direct effect on densification and pore change of sintering. Therefore, sintering power can also be studied from the angle of the evaporation-condensation of the material, that is, the difference of the saturated vapor pressure is used to express the sintering power.
By using the ideal two ball model and using the Gibbs Kelvin (Gibbs-Kelvin) equation, the difference between the saturated vapor pressure and the saturated vapor pressure of the surface is calculated as follows:
ΔP curve =-PγΩ/kTρ(1)
Where P-- Saturated vapor pressure of the plane,
γ-- Surface tension,
Ω-- Volume of a single vacancy,
k-- Boltzmann constant,
T-- System temperature,
ρ-- Radius of curvature of sinter neck.
When the radius of particle α is much more than the curvature radius of sintering neck ρ, the deficit between vapor pressure P and the plane vapor pressure on the surface is much smaller than ΔP curve, which can be ignored. As a result, the deficit between the vapor pressure on the surface and the vapor pressure on the surface of the neck (concave) can be approximated as follows:
ΔP=PγΩ/kTρ(2)
The vapor pressure difference causes the atoms to evaporate from the surface of the ball and re - sintered the neck concave to condense. It is a model that evaporates the migration of condensed matter, of which the evaporation rate is related to the vapor pressure deficit. The growth rate of the sintered neck increases with ΔP. Material transfer (the rate of condensation) can be expressed by the quality of objects condensed in unit area and in unit time m, of which the approximate calculation formula is as follows:
m=ΔP(M/2πRT)1/2(3)
Where M-- Atomic mass of matter,
R-- Gas constant.
When the growth rate of the sintered neck is represented by the increasing rate of the neck volume V, the formula is as follows:
dV/dt=(m/d)A(4)
Where A-- Surface area of sintered neck,
d-- Theoretical density of powder.
Joint Calculation
x3/a=Kt(5)
Where x-- Radius of sinter neck,
a-- Particle radius,
t-- Sintering time,
K-- Constant coefficient.
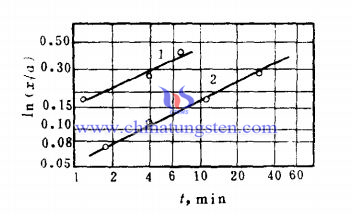
From formula (5), the characteristic velocity equation of the evaporation and condensation mechanism is the linear relationship between the three squares of the radius X of the sinter neck and the sintering time t.
- Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com