Acetone Affects Tungsten Oxide Crystal
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 09 February 2018 14:59
Acetone plays an important role in the growth of tungsten trioxide. The addition of acetone during the preparation of tungsten trioxide will result in the formation of tungsten oxide crystal cavities, which will cause the sample to lose its crystalline water. In general, tungsten oxide crystal growth is determined by its intrinsic crystal structure and external reaction environment.
In the reaction of tungsten trioxide, there are many external environmental factors that affect the crystal growth of tungsten trioxide. Such as the use of solvent properties. The solubility of sodium tungstate is a key factor in the crystal growth of tungsten trioxide. The higher the solubility of sodium tungstate, the more uniform the crystal nucleation of tungsten trioxide. The acidified sodium tungstate solution has very high solubility in acetone and can be miscible in any ratio. Acetone carbonyl with electronegativity, it can interact with tungsten ions. In addition, acetone has an effect on oxygen in the tungstate because of its high activity.
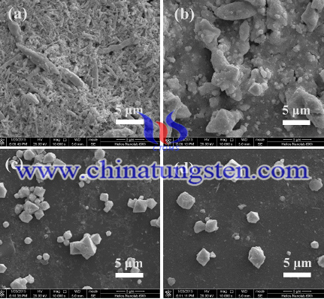
In the sodium tungstate water system, the tungsten trioxide crystal grows in its intrinsic direction, so the tungsten trioxide crystal face is exposed. When there is acetone in the sodium tungstate solvent, the tungsten trioxide crystal face is exposed due to the interaction between acetone and ammonium tungstate. Because different tungsten oxide planes have different growth rates, they result in two distinct morphologies of the same species. From this, it can be seen that acetone is adsorbed on the crystal face of hydrous tungsten trioxide so that the crystal face is retained. From the geometry of tungsten trioxide we can see that if the crystal face remains, then the tungsten trioxide sheet structure will be transformed into tungsten trioxide quasi-hexagonal sheet structure.

- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com