Sintering - Rearrangement of Particles
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 28 February 2018 14:35
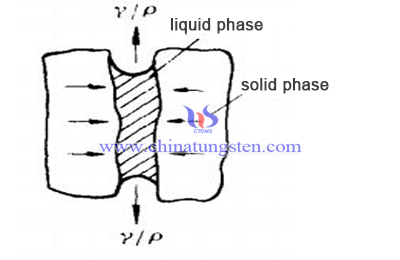
Mechanism of Solid Phase Sintering
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 28 February 2018 14:27
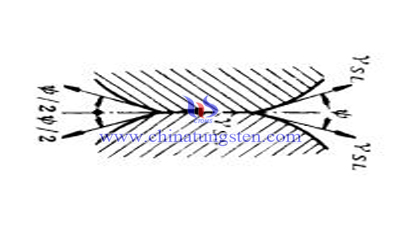
Mechanism of Solid Phase Dissolution and Reprecipitation
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 28 February 2018 14:23
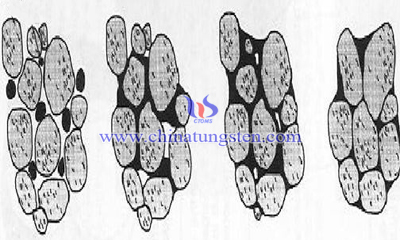
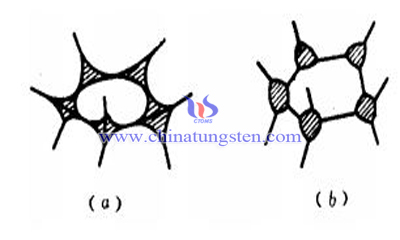
Influence Factors of Particle Pattern and Distribution
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 28 February 2018 14:19
Removal of Chromium from Tungsten Waste
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 28 February 2018 13:44

Recovering tungsten from tungsten waste has become an important measure to alleviate the shortage of raw materials. At present, the main ways to treat tungsten waste at home and abroad include mechanical crushing, electrolysis, alkali leaching, sodium roasting and zinc melting. Among them, sodium roasting technology is more mature and has wide applicability to waste tungsten materials. Therefore, this method is generally used to recycle tungsten carbide and various kinds of tungsten.
Liquid Form Synthesis of Tungsten Carbide
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 28 February 2018 13:06

Tungsten carbide is the main raw material for the production of hard alloy. The process of producing alloy powder in the tungsten production and processing enterprises is basically the combination of tungsten carbide powder and cobalt powder through mechanical mixing, and the uniformity of the alloy powder is not ideal. It has a great influence on the pressing of the subsequent cemented carbide. Some scholars have tried to pre - configure the alloy powder in the liquid state and then reduce the alloy powder.
Preparation Method of Tungsten Molybdenum Alloy Crucible
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 27 February 2018 20:39

Rare earth metal is an important resource and strategic resource in China. It is widely used in various fields and has been known as "industrial monosodium glutamate". Rare earth elements are highly active metals, which are usually difficult to be extracted from their compounds in general conditions. The electrolytic extraction requires the crucible and tungsten electrode.
Tungsten Oxide Structural Water Model
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 27 February 2018 14:34
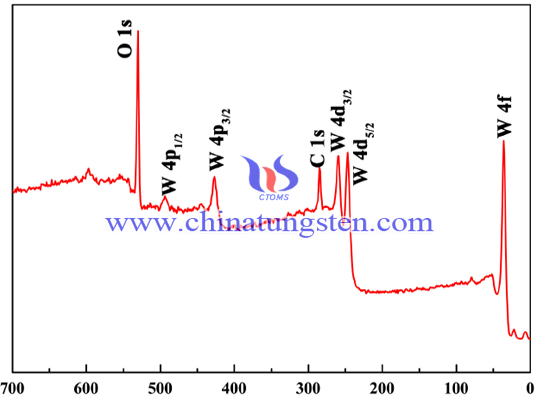
Structural water model of tungsten oxide produced by the hydrogen gas dehydrogenation of Pt catalyze the reaction of tungsten oxide and hydrogen on the surface of Pt: a part of hydrogen ions reacts with the oxygen ions on the surface of tungsten oxide to generate water molecules and release them from the film.
Tungsten Oxide Small Size Effect
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 27 February 2018 14:32

When the size of the tungsten oxide material is as small as nanometers, the tungsten oxide material exhibits different physical and chemical properties from those of conventional materials. Nano-sized tungsten oxide materials will produce small size effects, surface effects, quantum size effects and tunneling effects, resulting in new properties of acoustic, optical, electrical, magnetic and thermal properties.
Oxygen-deficient Tungsten Oxide
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 27 February 2018 14:23
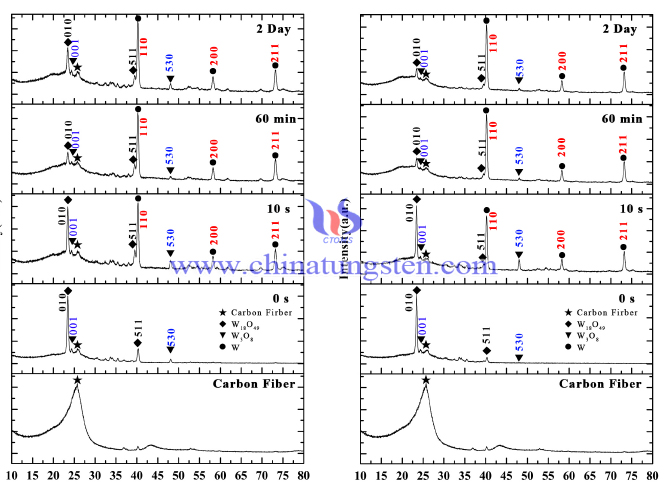
As an important semiconductor material, tungsten oxide has been widely applied to gas sensing, photocatalysis, electrochromic and field emission due to its special defect structure and chemical properties. There are some non-stoichiometric proportions of tungsten oxide in the actual preparation.


 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com