Tungsten Electrode
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 27 April 2019 21:32

Tungsten is one of the metals with the highest melting point and the most common arc electrode material. Tungsten electrode material is mainly used in tungsten argon arc welding. It is generally used as cathode part in the process of argon arc welding. It is almost suitable for welding all metal materials.
A Strategy for the Perfect Removal of Chromium from Waste Tungsten by Nitrate Melting
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 27 April 2019 21:28

With the rapid development of economy, the demand for tungsten metal materials is increasing. Almost all the metal elements constituting cemented carbide materials are rare elements. It is increasingly urgent to make comprehensive use of various tungsten resources. Over the years, the industry has done a lot of work on the comprehensive utilization and regeneration of tungsten resources. At present, the recovery and utilization of waste tungsten accounts for 20% of China's tungsten consumption. The regeneration and utilization of tungsten resources plays an important role in the national economy.
High Efficiency Recovery Model of Tungsten Waste
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 27 April 2019 20:57

At present, the method of extracting tungsten mostly adopts water immersion method. Before water immersion process, tungsten scrap needs to be sintered. The sintering process directly sinters the mixed powders. During the sintering process, the dust is discharged along with the flue gas, and the valuable metal tungsten is mixed in the dust, which results in the loss of valuable metal tungsten. The unreasonable ratio of raw materials to auxiliary materials leads to the low conversion rate of tungsten when tungsten waste is used to extract tungsten.
Tributyl Citrate Catalyzed by Phosphotungstic Acid Supported on Epoxy Resin
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 27 April 2019 20:51

Due to the defects of concentrated sulfuric acid catalysis, scholars at home and abroad have successively used strong acid cation exchange resin, heteropoly acid, inorganic salts, solid superacid as catalysts to prepare tributyl citrate. Comparing various methods, chemists believe that Heteropoly salts with Keggin structure are the best catalytic scheme. For example, phosphotungstic acid with Keggin structure is an oxygen-containing polyacid bridged by heteroatom P and coordination atom W through oxygen atom coordination unit. It has both the function of acid catalysis and oxidation catalysis. It is a protonic acid with uniform strength and high catalytic activity.
Epoxy Compounds by Tungsten Ionic Liquid Catalyst Preparation
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 27 April 2019 20:37
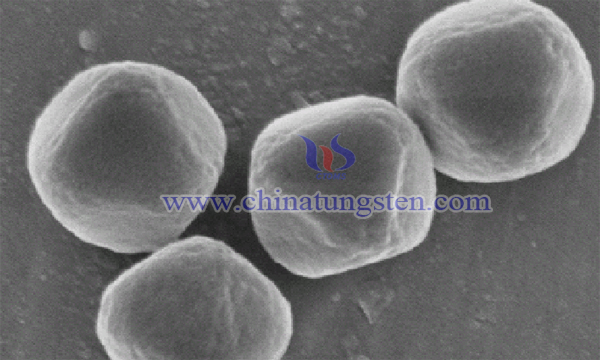
Epoxy compounds are important intermediates in organic synthesis and chemical raw materials. The ternary ring of epoxy compounds has special tension, so it is easy to synthesize many substances needed by people through selective ring opening or functional group conversion. Epoxy compounds have been widely used in many fields such as fine chemical industry, petrochemical industry, organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, spices and so on.
Ammonium Tungsten Bronze--Titanium Dioxide Composite Photocatalyst
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 27 April 2019 20:29

With the improvement of science and technology level and the progress of human development level, environmental pollution is becoming more and more serious, toxic and difficult to degrade. Pollutants are more and more widespread in the air, which is harmful to biological safety and ecosystem, and restricts the progress of society.
Medical Application of Nano Tungsten Disulfide
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 27 April 2019 20:19
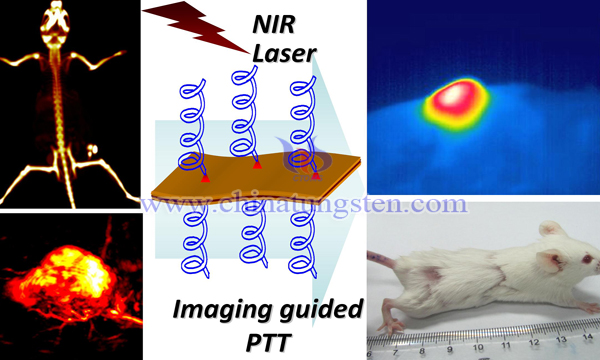
Since Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov won the Nobel Prize in Physics for their research on graphene in 2010, graphene-like transition metal sulfides MS2 (M=Mo, W, Nb, Ta) have attracted wide attention due to their unique physical and chemical properties.
Tungsten Oxide Pencil-like Nanostructure Arrays
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 20 April 2019 17:19

Tungsten oxide is an important semiconductor material. It is widely used in electrochromic devices, gas chromic devices, photovoltaic cells and other photovoltaic devices.
Tungsten Oxide Nanowire Catalyst
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 20 April 2019 17:09
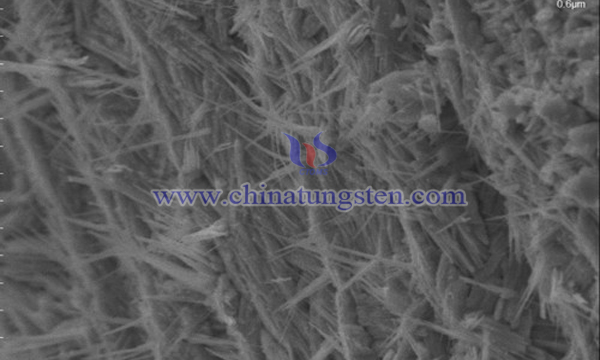
Due to the continuous consumption of fossil fuels and the increasingly prominent environmental problems, the search for clean and sustainable use of new energy has become an increasingly important topic. Among many new energy sources, hydrogen energy has become a research hotspot due to its high energy density, clean (water products) and sustainable utilization.
How to Prepare Tungsten Carbide--Carbon Composites
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 20 April 2019 17:03

Tungsten carbide has a catalytic activity similar to platinum. It has stable physical and chemical properties and low cost. With people's attention to clean energy, the application of tungsten carbide in catalytic fields, such as direct methanol fuel cell, catalytic hydrogen evolution, supercapacitor and catalytic desulfurization, has attracted extensive attention of scientists. For example, tungsten carbide as a catalyst can partly replace or to some extent save precious metals such as platinum and palladium, and its application prospect is broad.


 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com